In the last few months, the PC industry has been witness to some very exciting developments. Processors that were once considered fast (550-900MHz), have been supplanted by small squares of silicon which can easily run well over the 'magical' threshold of 2.0GHz. Still newer processors are on the drawing boards of chip designers which by the end of this year are expected to break the 3.0GHz+ barrier!
Along the way, there has been a push in the SDRAM manufacturing industry to have the present type of memory run faster, alongside the blazing processor speeds now available in the PC marketplace. The current iteration of SDRAM has begun to show its' limitations in memory bandwidth with both PC100/PC133 SDRAM platforms. By causing a bottleneck in the performance of these new processor speed demons, memory is starting to be the limiting factor to the question, "how fast can you go?"
DDRAM (Double Data Ram) evolved from the need to search out an alternative to SDRAM to free up this pressing bandwidth limitation.
Coinciding with this evolution came AMD with its' now
well
known line of processors - the Athlon and its stablemate, the Duron.
With these processors alone, AMD was able to garner numerous awards and praises
within the PC industry and gain strong acceptance by PC consumers in the
home and small office markets. The trend continues even to this day with the AMD
AthlonXP.
| DDRAM MEMORY |
|---|
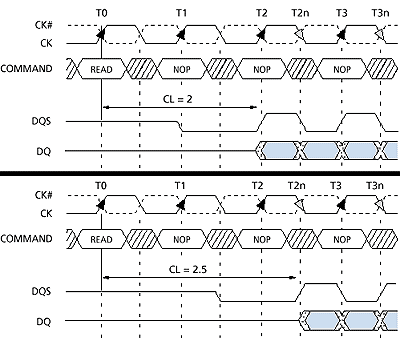 |
| DDR RAM timing for CAS2 and CAS2.5 DDRAM. Note the
vertical dashed lines which indicate an access of the memory. There are
two per clock cycle, whereas SDRAM has only
one. |
| SDRAM MEMORY |
|---|
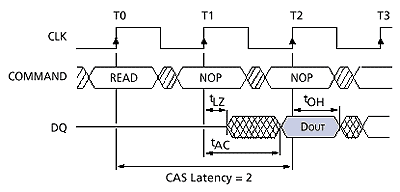 |
| With SDRAM all
signals to the memory are registered on the positive edge of the clock
signal (CLK). |
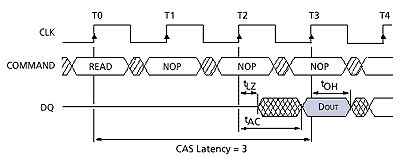 |
| CAS latency is the
delay between the registration of a read command and the availability of
the first piece of output data. CAS latency is measured in clock cycles.
This particular timing diagram represents SDRAM with a CAS latency of 3.
In this example a read command which is registered at T0 (Time=0) and will
not be valid until T3 (Time=3). Essentially, the lower the CAS latency the
better - this holds true for both DDR and
SDRAM. |

