| PCStats Heatsink Clearance Measurements |
| Top Clearance: |
9 mm |
| Bottom (cam) Clearance: |
7 mm |
|
| Left Side (arm) Clearance: |
20 mm |
| Right Side Clearance |
15 mm |
|
| Socket Mounting Holes: |
4mm Ødia. |
| Max. Heatsink Base Dimensions: |
~91x78 mm |
|
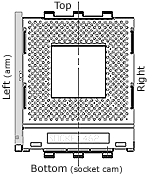 Note: Approx. measurements are made from the edge of the socket (not the clips) to the closest obsticle taller than the ZIF socket itself.
Note: Approx. measurements are made from the edge of the socket (not the clips) to the closest obsticle taller than the ZIF socket itself.
The socket is 51mm across, and 62mm from
top to bottom. |
| |
 |
The area around the Socket A is pretty tight where it
counts. There are a line of four 30mm tall capacitors about 9mm away from the
top of the socket so installation of medium to large heatsinks may
be very difficult. In testing, the Thermaltake Dragon Orb 3, a medium sized heatsink,
would not fit onto the socket because of capacitor interference. Slim and wide
heatsinks may be a better choice as there is substantially more space on the
left and right sides of the socket. Heatsinks which typically need to use the
socket mounting holes in the PCB won't really be applicable to the AN11
Stealth.
[Editors Note: Expect to see the
Heatsink Clearance chart on all future PCStats.com socket A motherboard
reviews.]
While there are a total of three fan headers on the board, one is used by the northbridge
heatsink leaving really just one available after the processors heatsink has been locked into place. It would have been nice to see at least one more fan header included on the board by the DDR slots for active memory cooling for instance.
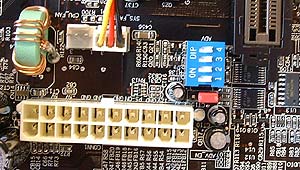
Oddly, the LED connectors on the motherboard
for the front bezel were apparently labeled wrong (first time I have ever seen this
happen), but after a quick glance at the manual things were straightened
out.
The AN11 Stealth comes with sound courtesy of VIA's AC'97
codec. The codec has a bad rap among hardware reviewers because it can put a drain on CPU resources, leading
to the inevitable PCI hardware soundcard upgrade.
There are a set of dip switches to control the
CPU voltage near the ATX power connector, and a ADV jumper. Another very important FSB jumper
by the BIOS (not shown) allows you to adjust the FSB of the
motherboard from 100 to 133MHz. The jumper is by default set to 100MHz, so if you drop in
an AthlonXP 2100+ you must change the jumper setting to
133MHz in order to realize the full clock speed of the AthlonXP. The AthlonXP
processors, in case you had forgotten, work at a 133MHz FSB.
Rounding out onboard features are Wake on Ring (WoR), Wake on
LAN (WoL) and support for IrDA.
