VIA's K8T800 is a more traditional chipset design than Nvidia's offering,
using separate Northbridge and Southbridge chips to carry out its functions. The
upgraded 'Pro' version that VIA released for the launch of the Socket 939 Athlon64 CPUs
is virtually identical to the original K8T800 chipset, and more or less
replaces it.
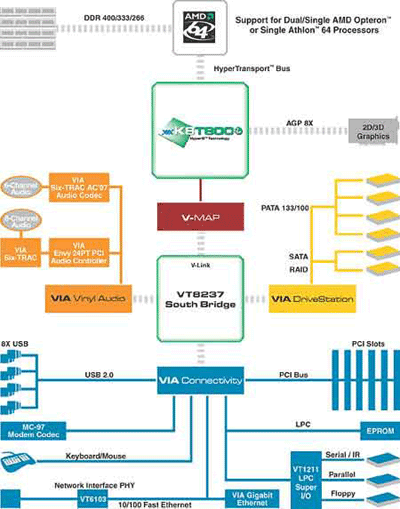
The major change is an increase in speed and maximum bandwidth for the
connection between the Northbridge chip and the CPU from 800MHz to 1000MHz, in
order to keep up with the speed of the new AMD offerings. A secondary change is
the doubling in speed of the proprietary 'V-link' connection between the north
and south bridge chips, reducing the possibility of a data bottleneck forming
between the two.
The only other difference between the K8T800 Pro and its predecessor is its
use of an asynchronous bus architecture, and the addition of a BIOS option for
locking the AGP and PCI buses together, keeping them in synch with each other
when overclocking, while they clock separately than the rest of the system. This
has made the chipset more popular with the enthusiast market through improved
overclocking potential.
As for features, the K8T800 Pro uses AGP 8X for graphics, with PCI-Express
again waiting for a later chipset design for its debut on AMD platforms. Up to
4GB of DDR memory is supported.
The VT8237 Southbridge Chip provides for up to a pair of serial-ATA drives,
as well as four standard ATA-133 devices. RAID is available for the serial-ATA
drives in RAID 0, 1 and 0+1 levels. A separate Serial ATA controller has to be
added by motherboard manufacturers in order to allow RAID 0+1 to actually
function, since 4 drives are needed.
Eight USB 2.0 connections are catered by four controllers. Onboard firewire
is not supported, but can easily be added by manufacturers.
VIA's 'Vinyl' integrated audio technology (compatible with AC'97) provides
integrated audio support. Manufacturers have a choice between the standard 6
channel 'six-TRAC' audio chip and the 'eight-TRAC' 7.1 channel chip.
Theoretically, the more high-end Envy audio chips could also be used, but in
practice this is rare.
The Southbridge chip is linked to the Northbridge chip by means of the new
'Ultra V-Link' proprietary connection method, which succeeds VIA's earlier
'V-link' connection seen on the original K8T800 chipset. The newer technology
offers double the bandwidth, 1066MB/s as compared to 533MB/s for the older
standard.
10/100 Ethernet is also integrated into the VT8237 chip. Gigabit-capable
parts may be added by manufacturers, but will need to be routed through the PCI
bus. Legacy support for floppy, parallel and serial ports (if implemented by the
manufacturer) rounds out the chipset's features.
From the specifications, you can see that the Nforce 3 Ultra is the more
feature oriented of the two competing chipsets, but features aren't everything.
Benchmarks should prove which is the better performer, but we doubt that there
is likely to be much difference between these two excellent chipsets. The next
generation of chipsets from these two companies should continue this fierce
competition, as well as introducing vital features like PCI-Express, and
SLI support.
Find out about this and many other reviews by joining
the Weekly PCstats.com Newsletter today! Catch all of PCstats
latest hardware reviews right here.
Related Articles
Here are
a few other articles that you might enjoy as well...
1. AMD Athlon64 3200+ 32/64-bit
Processor
2. AMD Athlon64 and AMD's 64-bit
technology
3. Intel Pentium 4 3.2GHz Extreme
Edition Processor
4. Intel Pentium 4 3.2E GHz Prescott
Processor
5. AMD AthlonXP 3200+ 400MHz FSB
Processor
