 The 80nm nVidia 'G84' core
at the heart of the MSI NX8600GT-T2D256E-OC videocard has 289 million transistors,
and according to nVIDIA documents a maximum power draw of
65W.
The 80nm nVidia 'G84' core
at the heart of the MSI NX8600GT-T2D256E-OC videocard has 289 million transistors,
and according to nVIDIA documents a maximum power draw of
65W.
That's 11W clear of
what the PCI Express x16 slot can provide (maximum 75W) and
why GeForce 8600GT videocards do not have an external power
connector.
The default clock speed of the nVidia GeForce 8600GT is
540 MHz (MSI clocks the core at 580 MHz), while the stream
processors hum along at 1.18 GHz.
The nVidia 'G84' core only comes equipped with
32 stream processors as opposed to 96/128 for the nVidia 'G80' core. The
memory runs at a flat 1.4 GHz (again overclocked by MSI to 1.6 GHz), yet with the
GeForce 8600GT the memory bus width is only 128 bits. That translates into a
slight memory bandwidth limitation, particularly at higher resolutions or with
visual effects like AntiAliasing enabled. Maximum memory size is supposed to be
256MB for all 'G84' based videocards.
While
the 'G84' core carries forward with nVidia's current thinking of how a graphics processor should
be built, there are a few notable changes from the 'G80.' Gone
are the hard coded Vertex and pixel shaders, they've been replaced with a
more flexible Stream Processor (or unified shader) that calculates both types of data. The
Stream Processors runs at 1.18 GHz incidently.  It's important to note that the GeForce
8600GT and 8600GTS GPUs have 32 stream processors each, while the GeForce 8800GTS
model has 96 and the 8800GTX 128. If you remember, 16 stream processors equals
one thread processor, so there are only two in the nVidia 'G84' core.
It's important to note that the GeForce
8600GT and 8600GTS GPUs have 32 stream processors each, while the GeForce 8800GTS
model has 96 and the 8800GTX 128. If you remember, 16 stream processors equals
one thread processor, so there are only two in the nVidia 'G84' core.
Each Thread Processor has two groups of eight Stream
Processors, and each group talks to an exclusive texture address filter unit as
well as well as being connected to the shared L1 cache. When more memory is
needed, the Thread Processor connects to the crossbar memory controller.
nVIDIA's crossbar memory controller is broken up into two 64 bit chunks for a
total bus width of 128 bits. By moving the GPU towards a threaded design, the
nvidia 'G84' is much more like a processor than any graphics core of the past. Any
type of data - be it pixel, vertex, or geometry shader can be processed within
the Stream Processor. This allows load balancing to occur between the various
tasks.
When it comes to videogames, we really just care that things look fantastic and move at
a quick pace. For that reason it's great to know that a mainstream GPU like
the Geforce 8600GT supports the following graphic must have's: nVIDIA's CineFX 5.0
shading architecture which includes unified vertex and pixel shaders, 64
bit texture filtering and blending, 64 bit texture filtering and blending, nVIDIA's UltraShadow
II and nVIDIA's Intellisameple 4.0 Technology. The card will
run at gaming resolutions as high as
2048x1536 at 85 Hz, and it supports nVIDIA's nView multi display capabilities. According to MSI,
the NX8600GT-T2D256E-OC has 22.4GB/s of bandwidth and a fill rate of 8.6
billion pixels. Wow.
nVidia PureVideo
HD:
As for miscellaneous core technologies, by default the
GeForce 8600GT supports HDCP over both DVI and
HDMI although the latter connector is up to the manufacturers discretion to
implement. The GeForce 8600GT model may or may not have HDCP support,
that is up to individual vendors. With the release of the GeForce 8600GT core, nVIDIA
is also updating its PureVideo technology. Dubbed "PureVideo HD" the videocard can now
handle the entire decoding processor of HD-DVD and Blu-Ray movies with
video playback with resolutions up to 1920x1080p. According to nVIDIA 100% of
high definition video decoding can be off loaded onto the videocard at speeds of
up to 40Mb/s.
According to nVIDIA when running two GeForce 8 series videocards in SLI,
PureVideo can be offloaded onto two GPUs for parallel
processing which should further decrease CPU load! nVIDIA's PureVideo HD
supports H.264 hardware decode acceleration as well as decryption for AES-128
CTR, AES-128 CBC and AES-128 ECB encryption found on Blu-Ray and HD DVD
discs.
To improve video quality, PureVideo HD also supports colour temperature correction
which should improve quality of colours. Thanks to Microsoft's Video Mixing
Renderer (VMR) support (later dubbed Enhanced Video Renderer in Vista), you
can watch several high definition videos at the same time. Finally, the GeForce 8
series GPU has built in HDTV support. Although it's up to the manufacturer to
implement it onto the videocard as usual.
As it is PureVideo HD will be of benefit to Blu-Ray/HD-DVD
type movies only, and does not boost WMV9 playback at this time. That means high
definition videos using the Microsoft standard will only be accelerated to
previous PureVideo levels.
Examining CPU Load with PureVideo
To test PureVideo's High Definition
accelerating capabilities on the MSI NX8600GT-T2D256E-OC videocard, PCSTATS will
play back a video downloaded from Microsoft's WMV HD Content Showcase
through Windows Media Player 10. "The Discoverers" (IMAX) video is available in
both 720P and 1080P formats. AMD processor utilization will be monitored via
Task Manager.
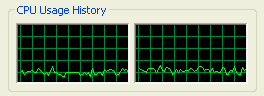
When running the 720P version of the
Discoverers video, CPU usage jumps between 15-18% which is pretty low and in
line with the other nVIDIA GeForce videocards that we've tested in the last
year.
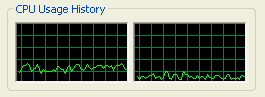
The 1080P version of the Discoverers video
uses even less CPU usage, here we're looking at between 13-15%! That's some
pretty good CPU usage numbers and you'll have no problems running things in the
background. Up next, overclocking the MSI NX8600GT-T2D256E-OC
videocard!
