
|
MSI's 785GM-E65 motherboard is built around the AMD 785G and SB710 chipsets, and features 128MB integrated DDR3 SidePort memory. MSI has adapted the AMD 785G chipset into a micro-ATX form factor, an ideal size for small home and office computers, and best of all Home Theatre PCs.
80% Rating: 
|
|
|
|
Home >
Reviews >
Motherboards >
MSI 785GM-E65 |
|
|
Overclocking the Motherboard and IGP, BIOS screenshots
 |
| Overclocking Results: |
|
|
Unlike
most integrated motherboards PCSTATS has reviewed, ATI has enabled IGP
overclocking with the AMD 785G chipset. The default clock is 500MHz, so it will
be interesting to see what impact an overclock will have on IGP performance.
We
started off by dropping the multiplier on the multiplier on the AMD Phenom II x4
955 Black Edition down to 8x, disabling features like Cool'n'quiet and CPU C1E
power states. A set of DDR3 memory modules from Corsair were locked into the MSI
785GM-E65 and set to run in DDR3-800MHz mode so it wouldn't hold the CPU back -
in this first test we're trying to find the highest support bus speed.
The bus
speed of the MSI 785GM-E65 motherboard was then bumped up from 200MHz to
250MHz.... and finally 260MHz. Not a great overclock, hopefully with future BIOS
revisions it will be possible to pus MSI's 785GM-E65 board a little further than
that!
Integrated Graphics
Overclocking
After finishing with the CPU, it was time to turn our
attention to the Radeon HD 4200 IGP. AMD IGPs tend to be very good overclockers,
so we had high hopes when approaching the new AMD 785G chipset.
 There are a number
of IGP overclocking options in the MSI 785GM-E65's BIOS dedicated to performance
tuning, including Sideport memory speed adjustment and voltage tweaking. Given
that this is an integrated graphics chipset (the northbridge is also interfacing
with the processor and controlling the PCI Express lanes) we took the prudent
route and left most of the voltage tweaking options alone. There are a number
of IGP overclocking options in the MSI 785GM-E65's BIOS dedicated to performance
tuning, including Sideport memory speed adjustment and voltage tweaking. Given
that this is an integrated graphics chipset (the northbridge is also interfacing
with the processor and controlling the PCI Express lanes) we took the prudent
route and left most of the voltage tweaking options alone.
Through simple adjustments of the core clock speed, it
was possible to take the Radeon HD 4200 IGP from its 500MHz clock speed up to an
initial overclock of 600MHz. Confident that the IGP could handle a lot more, we
quickly sped through 700MHz and attempted an 800Mhz overclock... but quickly
found that random screen freezes and graphical corruption telling us we had
gotten overly ambitious. Eventually we found that a 750MHz overclock was an
acceptable speed that stayed solid during benchmarking.
While with voltage tweaking there are certainly
possibilities to push the Radeon HD 4200 IGP even further, most users should be
aware that such extreme overclocking carries some risks of damaging components
and the motherboard's overall lifespan. Even at stock speeds the
passively-cooled AMD 785G chipset got quite warm during 3D benchmarks, and we do
not recommend increasing the chipset voltage without some kind of active chipset
cooling.
As a final note, while an IGP like the Radeon HD 4200
may be capable of hitting some extreme speeds, at the end of the day it's still an IGP. Even when overclocked, an IGP with
only 40 shader process won't match the performance of most mainstream
videocards.
Inside the BIOS of the MSI
785GM-E65
The MSI 785GM-E65's BIOS has control over all of the
major features of the AMD 785G chipset, including IGP and Sideport memory
overclocking.
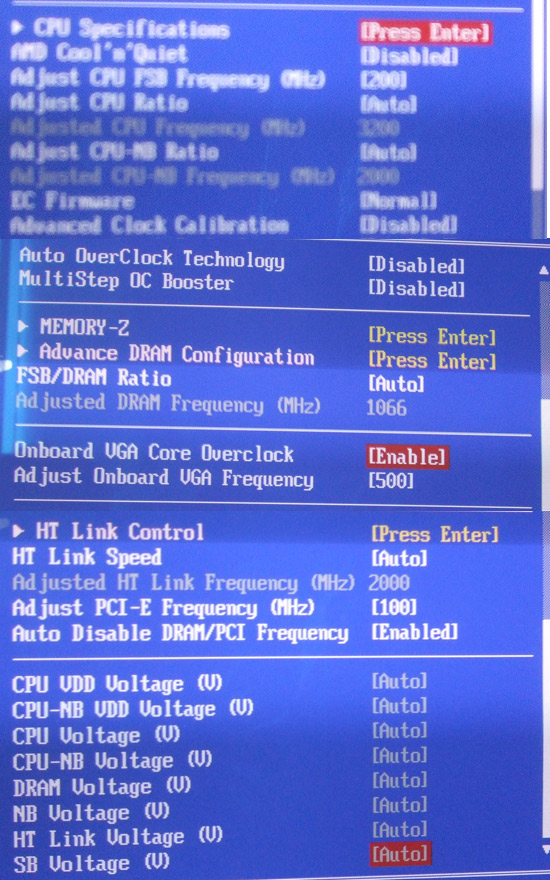
MSI calls the main overclocking page the Cell menu, and
it has pretty much every feature you need for adjusting the system clockspeeds,
timings and voltages.
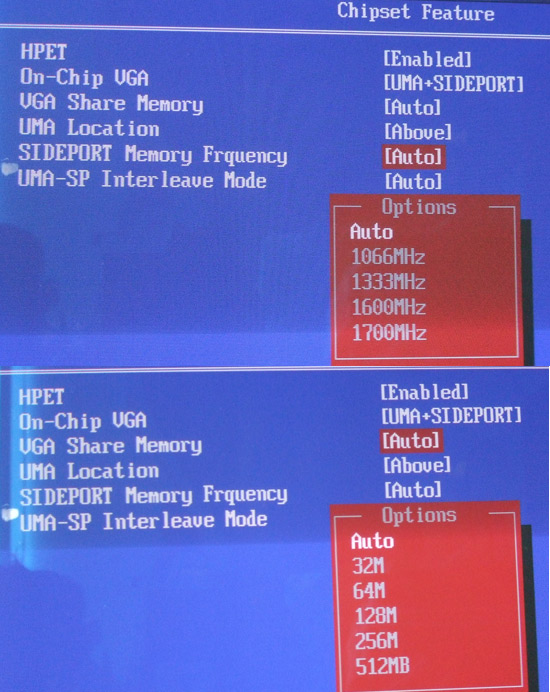
The Radeon HD 4200 IGP can be tweaked pretty
extensively. The 128MB of Sideport memory can be overclocked to increase its
performance, and the amount of main system memory the IGP shares can be adjusted
to suit the needs of your computing.
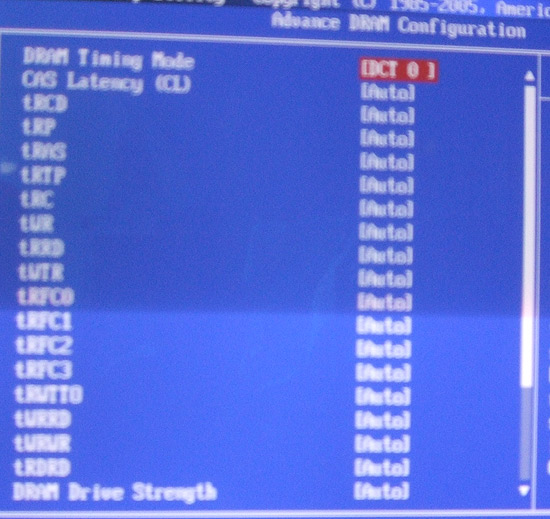
Memory timings can be adjusted by clock cycle.
Tightening memory timings reduces latency and improves overall memory
performance.
|
