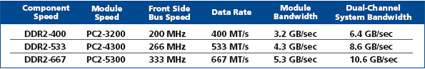
The chart here shows the naming conventions and
specs for the first three DDR2 standards to be released. Notice that DDR2-400
features exactly the same bandwidth as DDR-400 memory. More on this in a
moment.
DDR2 memory modules will start off at 256MB capacities, with 512MB and
1GB available. The standard is capable of considerably higher memory densities
though; modules of up to 4GB are defined in the specifications, and are
available for specialized applications (though these will not be compatible with
desktop chipsets, for the time being at least). Higher capacities should be
achieved in the future.
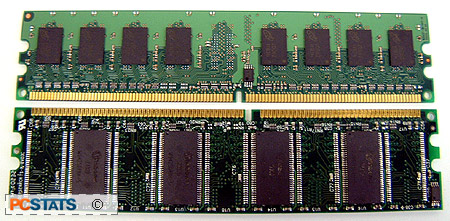
All DDR2 memory chips (called DRAM) will use the
FBGA (Fine Ball Grid Array) method of packaging, allowing higher memory
densities in considerably smaller chips, with better electrical and
thermal properties. Some DDR modules use this method now, but it becomes
part of the standard with DDR2.
 The older style
associated with DDR, and SDRAM, is the TSOP-II package, shown on the lower
memory module above. Also note the differences in the number of gold electrical
contacts along the leading edge of each module.
The older style
associated with DDR, and SDRAM, is the TSOP-II package, shown on the lower
memory module above. Also note the differences in the number of gold electrical
contacts along the leading edge of each module.
