Since the motherboard controls what options you have for overclocking, it's
essential to take a look at the BIOS (Basic I/O System) pages of the board to
examine the options available.
Reboot the computer and go to the BIOS screen by pressing the DEL key
repeatedly during startup.
Note that some motherboards respond to different key commands to bring up the BIOS. Dell computers for example often rely on F2 or F8, while other manufacturers may opt for F10 to bring up the BIOS.
When the BIOS comes up on the screen you will be greeted with a blue menu with about a dozen headings. Navigate through the list by using the arrow keys, and press 'enter' to select a menu. When you're done press the ESC key to exit, and either save or discard any changes you've made to the BIOS settings.
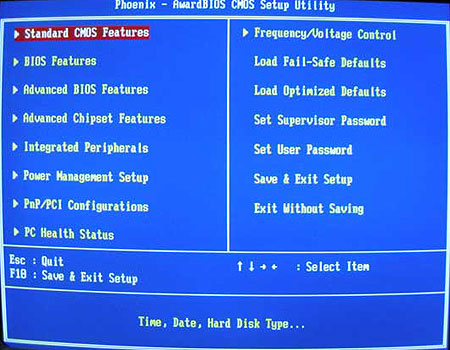
The first features to look for are CPU and FSB speed adjustment controls.
Generally, these will be in a section of the BIOS called 'frequency/voltage
control'.
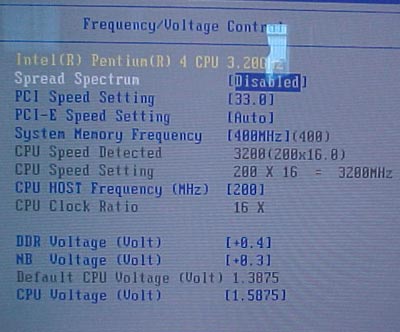
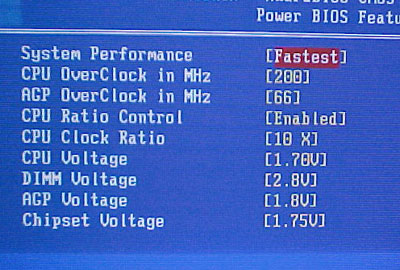
CPU bus frequency setting and DDR voltage
options are on the following screens, on the next page.

