Of all the AMD 8-series chipsets, the AMD 890FX is the one
specifically designed for performance enthusiasts and hardcore gamers.
Here's why; the first AMD 800-series chipsets linked together an integrated
graphics processor (IGP) with support for add-in (discrete) graphics. The AMD
890FX chipset on the other hand is dedicated to discrete videocards only.
Instead of the Radeon HD 4290 IGP the 890FX features 42 lanes of PCI Express 2.0
bandwidth.
If you've been looking for an AMD setup to handle high-end quad-CrossfireX
configurations, your prayers have just been answered.
AMD 890FX-based motherboards will have two major configurations: the more
common configuration will have a pair of PCI Express 2.0 x16 slots, each with
x16 lanes of bandwidth. Variant versions will have four PCI Express 2.0 slots
which can run in (x16/x16/x0/x0) mode, or in (x8/x8/x8/x8) mode for four-way
CrossFireX configurations.
All of this PCI Express 2.0 bandwidth comes in handy because today's graphics
cards are pushing ever-more amounts of bandwidth along the PCI Express bus.
Top-end enthusiast videocards like the dual-GPU Radeon HD 5970 can be
bottlenecked by the limited bandwidth of a PCI Express 2.0 x8 connection, with
significant drop-offs in peak performance and lower overall frame rates. This
performance penalty gets even worse if you're trying to run a pair of high-end
videocards in CrossfireX mode, the videocards will completely saturate the
(x8/x8) PCI Express, and you'll never get the most out of your expensive
eye candy generators.
|
AMD 700 and 800-series Chipsets
|
|
AMD 790FX |
AMD 870
|
AMD 880G |
AMD 890GX |
AMD
890FX |
| CPU |
Socket AM2 |
Socket AM2/ Socket AM3 |
Socket AM3 |
Socket AM3 |
Socket AM3 |
| Memory |
1066MHz DDR2 |
1066Mhz DDR2/ 1333MHz DDR3 |
1333MHz DDR3 |
1333MHz DDR3 |
1333MHz DDR3 |
| Graphics Expansion |
2x16 PCI Express 2.0 |
1x16 PCI Express 2.0 |
1x16 PCI Express 2.0 |
1x16 PCI Express 2.0,
2x8 PCI Express
2.0 |
2x16 PCI Express 2.0,
4x8 PCI
Express 2.0 |
| Peripheral Expansion |
6x1 PCI Express 2.0 |
6x1 PCI Express 2.0 |
6x1 PCI Express 2.0, 2x1 PCI Express 2.0 on
SB850 |
6x1 PCI Express 2.0, 2x1 PCI Express 2.0 on
SB850 |
6x1 PCI Express 2.0, 2XPCI Express
2.0 on SB850 |
| IGP |
- |
|
Radeon HD 4250 |
Radeon HD 4290/RV620 |
- |
| Process |
65nm |
65nm |
55nm |
55nm |
65nm |
| TDP |
10W |
12.5 |
18W |
25W |
19.6W |
| IOMMU 2.0 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
Yes |
| Southbridge |
SB600 |
SB710 |
SB710 |
SB850 |
SB850 |
| Storage |
4xSATA 3Gb/s |
6xSATA 3Gb/s |
6xSATA 3Gb/s |
6xSATA 6Gb/s |
6xSATA 6Gb/s |
| USB |
10x USB 2.0, |
12x USB 2.0 |
12X USB 2.0, 2 USB 1.1 |
14x USB 2.0,
2x USB 1.1
|
14X USB 2.0,
2x USB
1.1 | | |
Like AMD's 890GX
chipset, the AMD 890FX northbridge had an extra pair of PCI Express 2.0 x1 lanes
which manufacturers can dedicate to SuperSpeed USB 3.0 ports (not in the Biostar
TA890FXE's case though).
IOMMU 2.0 support also makes its debut with the AMD 890FX
chipset. IOMMU is a memory allocation and isolation technology that can benefit
virtualization and data integrity. Devices can take advantage of IOMMU to use
native drivers in a virtualized environment, improving overall performance.
IOMMU can also prevent devices from erroneously overwriting critical data, like
kernel pages. IOMMU is currently a feature that hasn't made its way into
consumer operating systems yet, but you can find if in certain Linux distros.
AMD has also indicated that the 890FX chipset
is a stronger overclocker compared to its previous chipsets, and is designed to
handle power loads more effectively. Since the AMD 890FX is the chipset of choice
for use with six-core processors like the Phenom II X6 1090T, getting a good
overclock could make for some some extreme performance gains. PCSTATS will be
testing out the 890FX's overclocking capabilities a little later on in this
review.
AMD SB850
Southbridge
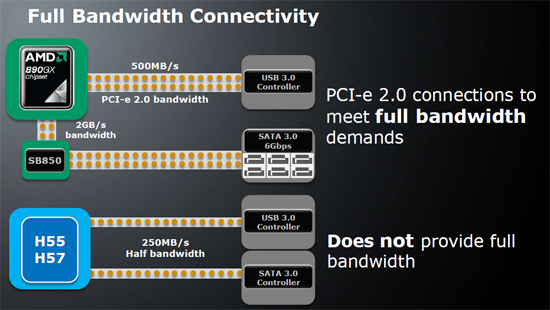
AMD's 890FX northbridge will be paired with the same AMD SB850 southbridge
that made its debut with the AMD 890GX chipset. The AMD SB850 is the first
southbridge to have native SATA 6Gb/s connectivity with full RAID support. With
all of the extra bandwidth that the SB850 southbridge controller is taking on,
AMD has also doubled the bus speed between it and the 890GX northbridge. This
expanded northbridge-southbridge bus has 16Gb/s transfer rates and is called
A-link Express III.
|
AMD SB850 Southbridge
with native 6Gb/s SATA III.
|
Similar to early support for USB 3.0, certain board
manufacturers 'bolted' SATA 6Gb/s controllers onto other chipsets, but
benchmarks have brought to light a number of compromises. The AMD SB850
controller has native SATA 6Gb/s support built in, which theoretically means no
compromises are necessary to enjoy faster storage drives, especially those
expensive Solid State Drives.
A fast SSD in sequential read mode can saturate the SATA 3Gb/s connections
found on typical motherboards, so SATA 6Gb/s support is more important than ever
to avoid bottlenecks. Towards the end of 2010 new 25nm flash production
techniques will make SSDs have larger capacities and lower prices then ever
before, so having the ability to connect SSDs at full speed is good for future
proofing your PC. Right now they are still very much a luxury item, but new
features like SATA 6Gb/s are always about having the foresight to look forward 6
or 12 months.
The SB850 southbridge supports SATA 6Gb/s in RAID 0, 1 5 and 10 modes, so you
can even set up a massive array of SSDs or conventional hard drives. SATA 6Gb/s
connections are backwards compatible with SATA 3Gb/s and SATA 1.5Gb/s hard
drives, although to take full advantage of the faster bus you need to match up a
SATA 6Gb/s capable hard drive with a SATA 6Gb/s connection to the motherboard.
Let's start off with a quick stroll around Biostar's
TA890FXE motherboard, then PCSTATS will dive into Overclocking, BIOS features and benchmarks!
