 Intel Smart Response Technology was
configured on the Gigabyte GA-Z68XP-UD3-iSSD motherboard with the included Intel
20GB SLC-flash memory mSATA SSD.
Intel Smart Response Technology was
configured on the Gigabyte GA-Z68XP-UD3-iSSD motherboard with the included Intel
20GB SLC-flash memory mSATA SSD.
A fresh installation of Microsoft Windows 7 was installed
to a standard Western Digital WD740 Raptor SATA hard drive while the PCH SATA
Control Mode was set to RAID(XDH) mode.
[For a detailed look at Intel SRT
thoroughly please read this PCSTATS Beginners Guide: Intel Smart
Response Technology and Intel 311 Larson Creek SSD ]
Setting up SSD Caching via
Intel Smart Response Technology
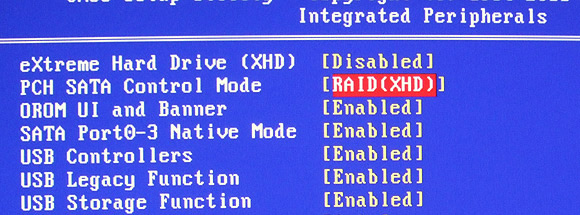
Setting up Intel Smart Response Technology is pretty
straightforward since the SSD is already installed to a mSATA port. In the BIOS
of the Gigabyte GA-Z68XP-UD3-iSSD motherboard all you need to do is configure
the 'PCH SATA Control Mode' to 'RAID(XDH)' and make sure the system boot off the
hard drive.

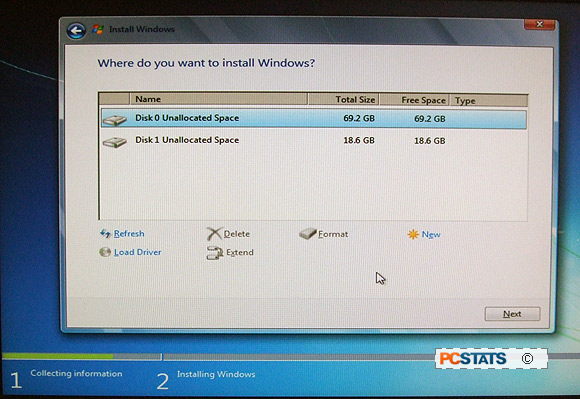
Reboot the PC and start the Windows 7 installation
procedure as normal. When it comes time to specify the installation hard drive
choose the mechanical HDD for the OS. Leave the cache SSD as unformatted and
unallocated space.
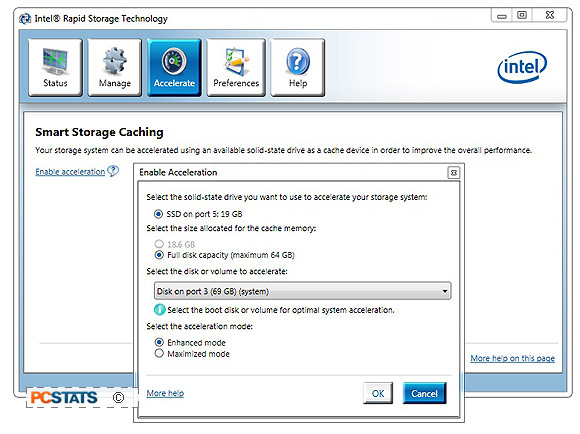
After Windows 7 is installed and you've applied all the
necessary hardware drivers and OS updates, install Intel Rapid Storage Technology and Intel Management Engine Software. Launch the 'Intel
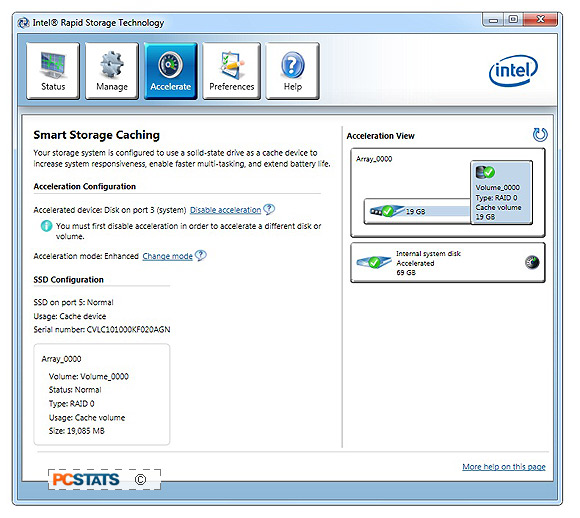
Rapid Storage Technology' program and click on the 'Accelerate' button at the
top (see below). Next, click on 'Enable acceleration > choose the 'disk
volume to accelerate' on which you've installed Windows 7 (in this example, Port
3 69GB - a Western Digital WD740 Raptor) > choose 'Enhanced Mode' and click
'ok'.
Enhanced Mode is the safest choice (Maximized Mode offers
an edge but there is risk of data loss), with it there is no possibility of data
loss in the event of a power failure as all cached data is written to both the
HDD and caching SSD.
In Maximized mode data is stored to the SSD before being
written to the HDD, so in the event of power outage Intel says data loss would
be about the same as if running RAID 0 with disk write cache enabled.
Intel SRT Failure
Recovery
After a forced hard power reset in an attempt to see just
how robust this Intel technology is, PCSTATS managed to trigger the Intel SRT
Option ROM which automatically began a self-repair action. The system was
configured to Intel SRT Enhanced Mode and took a few minutes to successfully
'rebuild' the Cache Metadata before it booted back into Windows 7 without
issue.
Below is an example of what may happen if there is a
power failure to an Intel SRT enabled computer system. Unlike Microsoft, when
Intel develops a technology it tends to make it very fault tolerant and
self-repairing. :)
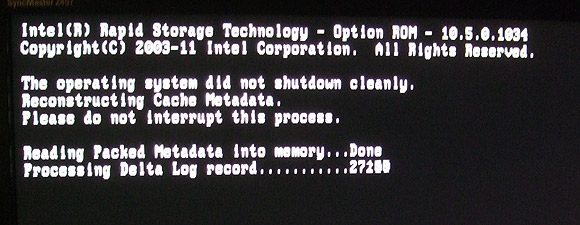
Intel SRT Failure
Recovery Screen
Disabling Intel Smart
Response Technology
If you ever wish to reclaim the cache SSD for storage
space and disable Intel SRT altogether, it's as easy as clicking the "Disable
Acceleration" link in Intel's Rapid Storage Technology Manager. This will revert
the 20GB Intel mSATA SSD back to standard storage device and delete all cache
data that was previously stored on the SSD.
Benchmarking Intel
SRT
