Security in the GN-B49GU is
governed by a screen of check boxes which enable and disable various
settings. Unfortunately, the language used to describe these settings is
confusing at best. In this area more than any other, we were left unsure
as to what each function actually did. The manual was no help either,
unfortunately.
We got in touch with Gigabyte,
informed them of our difficulties and they gave us the information we
needed:
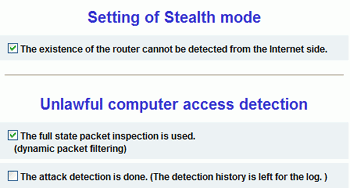
The
'setting of stealth mode'
function is straightforward, stopping systems outside the network from pinging
the router successfully and hiding exposed ports.
The
'access of a set screen of this machine from the WAN side is
prohibited'
checkbox is also straightforward,
cutting off access to the router's console from the Internet.
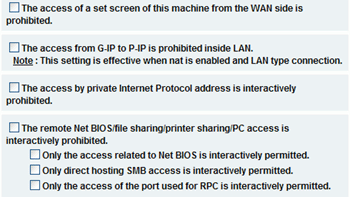
'The
access by private Internet Protocol address is interactively prohibited'
restricts private IP addresses (192.168.x.x etc.) from passing through the WAN
side of the connection into the routers network. This is not a situation
that would come up unless you were using the router to separate private
networks. 'The remote Net BIOS/file sharing/printer sharing/PC
access is interactively prohibited'
disables file and printer
sharing from outside the router's network by stopping the related protocols from
passing through the router.
'The
attack detection is done'; when
this is checked, the router will watch for denial of service attacks (floods of
identical traffic from a single source) and cut them off, and will
also log the attack.
'The
access from G-IP to P-IP is prohibited inside LAN'
this one was a mystery to us
at first. Turns out that this is a part of the router's support
for having multiple global IP (legitimate internet) addresses inside the network.
Some ISPs in Japan and a few other places provide this ability. The
security feature prevents the global IP computers from communicating with the private IP computers
within the network, a safeguard in case the global IP systems are
compromised from the Internet.
Stateful packet inspection can also be enabled on the
GN-B49GU. By definition, this means that the firewall examines incoming and
outgoing packets in comparison to previous network traffic as well as a static
list of rules. This type of firewall can catch things like the flooding of
identical traffic (denial of service attacks) and Trojan horses sending data out
from inside the network.
