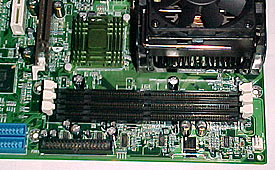
SDRAM Memory
The EP-4B2A can
support up to three PC133 SDRAM modules of 1.0GB in size.
Heatsink Mounts
With the introduction
of the newer socket 478 Pentium 4 architecture, motherboard manufacturers had to yet again redesign their
layouts to support large heatsinks. The socket 423 and socket 478 architectures are not compatible by
nature, but different heatsink manufacturers may offer dual purpose heatsinks. In any case,
the small socket 478 is really too tiny to attach anything to, so a standoff is mounted
to the PCB which the heatsink attaches directly to.
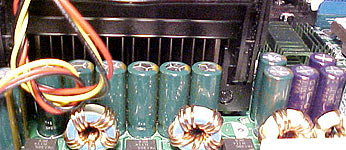
The
proximity of capacitors to the processor has always been a bit of a double edged
sword. The closer the capacitors are, the more interference is filtered out. The
problem with this from a cooling perspective is that, closely placed capacitors
can interfere with airflow around the processor, potentially leading to higher running temps. While the situation
is much more controlled than on AMD boards where some heatsinks won't even fit
on the board, draping power cables and capacitors can still muck up ideal
air flow patterns.
 |
|
The processor
socket is closely surrounded by tall capacitors on one side, potentially
causing air flow issues. The 12V ATX and 5V/3V ATX power connectors are located centrally on the
board and don't really get in the way.
|
Fan Headers
There are a total of
three fan headers on the 4B2A. One is taken up by the processor
heatsink, while the other two remain free for use with system fans,
or graphics card cooling. Two fan headers are positioned near to the processor socket
itself, and the third lies on the lower end of the board.
Sometimes
these important little fan connectors
can get stuck in the most awkward of places, but this wasn't the case with
the Epox mainboard. All of the fan headers are easily reachable and the need
for super small fingers or tweezers in not necessary whatsoever.
i845 Heatsink
Thermally, the i845 chipset is only
cooled by a lowly green BGA cooler, and one with no thermal compound either. We weren't impressed by
this 'solution' very much needless to say. Personally, I would remove this cooler and
at least put down a coating of some good quality silicon thermal compound. The green BGA cooler
is attached directly to the PCB by means of small plastic pegs, so it can be
removed - just be careful not to chip the small i845 core while doing so.
|

|
|
The i845 chipset heatsink is simply a
larger version of the generic green passive heatsinks we all
know and hate. Epox
use no thermal interface materials, but just stick the thing on
top of the silicon core. |
