Legacy Mode includes no 64-bit
support at all, effectively closing off access to the upper half of the
processor's registers. It is completely compatible with 32-bit x86 software.
 Long mode is made up of two sub modes,
Compatibility mode and 64-bit mode. Compatibility mode is designed for a 64-bit
operating system such as Microsoft's impending 'x64 edition' of Windows XP and
Microsoft Server 2003 running 32-bit software. The beta version of 64-bit XP
supports 32-bit executables through the use of this mode.
Long mode is made up of two sub modes,
Compatibility mode and 64-bit mode. Compatibility mode is designed for a 64-bit
operating system such as Microsoft's impending 'x64 edition' of Windows XP and
Microsoft Server 2003 running 32-bit software. The beta version of 64-bit XP
supports 32-bit executables through the use of this mode.
When running in this mode, each
32-bit application is still limited to 4GB of memory, but it can have all of
that 4GB to itself with no overhead for the operating system (assuming that
there is more than 4GB of memory installed).
The OS will use the memory
space over 4GB which cannot be addressed by 32-bit apps. This provides a great
shot in the arm for servers using demanding 32-bit applications, like databases,
which cannot be easily changed over to 64-bit operation. 64-bit mode is intended
for a pure 64-bit environment, both operating system and software. The AMD64
architecture allows a processor running a 64-bit operating system to switch
seamlessly between these two sub modes.
Inside the Athlon 64 processor
 In September of 2003, the AMD Athlon 64/FX line of
processors brought the flexibility of the AMD Opteron processor to the home and
enthusiast markets.
In September of 2003, the AMD Athlon 64/FX line of
processors brought the flexibility of the AMD Opteron processor to the home and
enthusiast markets.
As a fully functional 64-bit release of Windows XP
or Server is still a year or more off, and the next version of Windows is
farther still, 32-bit compatibility is a good thing. Likewise for Linux
enthusiasts who now had the hardware to exploit its full capabilities within
their reach.
Still, people wondered if the
AMD Athlon 64 would bring anything to the table besides 64 bits of potential for
the future. They needn't have worried. The architecture of the Athlon 64 is
radically different from conventional 32-bit processors, and the changes that
AMD made benefit 32-bit performance as well as enabling 64-bit operations.
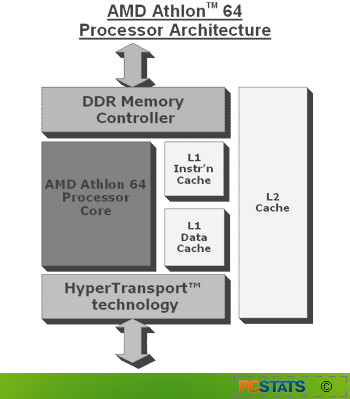
The first of the two main
changes was the relocation of the memory controller off the motherboard (where
it traditionally resides in the Northbridge chipset) and into the processor die
itself. Thus the processor gained the advantage of unrestricted access to
memory.
In previous designs, data traveling to and from the
memory controller and the memory itself had to pass through the Northbridge chip
and across the bus linking it to the processor. This same path is shared by data
from every other peripheral attached to the system. As you can imagine,
information bottlenecks often resulted.
