The second major innovation was
the introduction and use of Hypertransport technology within the chip.
Hypertransport is a serial bus technology which provides for high-speed
point-to-point connections between specific computer components within a system.
It is both faster and (theoretically) cheaper to implement than conventional
parallel data bus methods.
Similar to PCI-Express , Hypertransport is scalable (meaning that additional data
paths can be added to create faster connections where required) and uses
'packets' to send data. In this it is like conventional Ethernet technology, in
which the data to be sent is encapsulated in additional layers of information
indicating where it's from and where it's going.
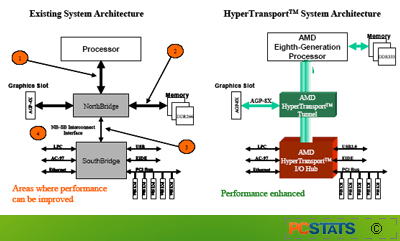
AMD chose to use Hypertransport
for the connection between the processor and the motherboard, thus replacing the
conventional 'front-side bus' parallel link. In combination with the removal of
the majority of memory traffic from this bus, this provides for a substantially
faster route between the processor and the rest of the hardware in the
system.
Current AMD Athlon 64
processors are available in both regular and Athlon FX models. AMD has gone
through three different socket designs for these two processor lines; 754, 940
and now 939 pins. The main difference between the FX and the regular Athlon 64
is the amount of Level 2 cache memory onboard. Current Socket 939 Athlon 64
chips have half the amount that the FX processors contain.
Older examples of the Athlon 64 for socket 754 had
a full megabyte of level 2 cache like the FX processors, but were limited by
their single channel memory controllers. The newer Athlon 64 processors for the
socket 939 form factor have dual channel memory controllers but less cache. I
suppose AMD has to keep its products separated somehow....
It looks like socket 939 will
be the choice processor for the near future of AMD's 64-bit chips, as they have
committed to releasing processors for the platform up until at least the middle
of 2005 for certain.
Extra Registers for 64-bit
The AMD Athlon 64 chip, like
the Opteron processor, has one large additional performance advantage when
operating in 64-bit mode. That is the 8 extra registers which exist, exclusively
for use with 64-bit code. This extra memory space in the heart of the processor
definitely gives it a performance boost when using 64-bit benchmarks, as our
results later in the article bear out.
