Intel's H67 chipset was released in
unison with the highly anticipated 32nm Intel 'Sandy Bridge' architecture
in early 2011. What set Sandy Bridge apart was
its integrated graphics core, a first in the desktop world. The
graphics core, or iGPU, shares some L3 cache with the four processing cores of
the CPU proper and due to these architectural changes a new CPU socket was also
born - socket LGA1155. Since its release, the Intel Core i3/i5/i7
2xxx-series Sandy Bridge processor has met
with fantastic success and given AMD a real run for its
money.
Yet in spite of its success, Intel integrated graphics still don't compete very well against discrete
graphics cards, even a $50 mainstream graphics card. So why do it like this? The upshot
of a CPU with an integrated graphics core is reduced cost for the majority of PCs sold by
the likes of Dell and large system integrators. After all, consider
that 70% of the total volume of PCs sold today feature integrated
graphics!
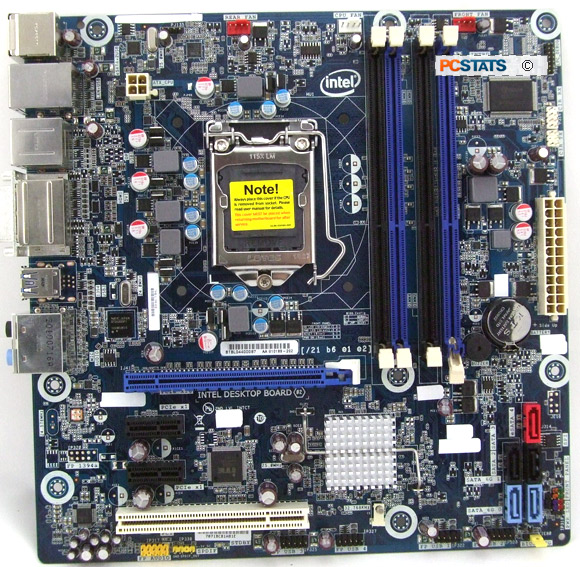
Motherboards like the Intel DH67BL that PCSTATS is
reviewing today support one PCI Express 2.0 x16 videocard, but more likely than not will never
see a discrete graphics solution. The DH67BL motherboard has one DVI-I and HDMI video
output.
Intel's DH67BL motherboard is built around the Intel H67
chipset and supports socket LGA1155 Intel 2nd Generation Core i3/i5/i7
2xxx-series 32nm Sandy Bridge processors. It is not compatible
with LGA1156 processors. On the storage front, the board offers up two
6Gb/s SATA III ports, three 3Gb/s SATA III ports and one eSATA III port. A
UEFI BIOS ensures support for hard drives larger than 2TB.
Dual USB 3.0 ports are handled by a discreet NEC controller
as USB 3.0 is not natively supported by the Intel H67
chipset.
 |
|
Intel DH67BL
Motherboard |
|


|
|
|
|
INCLUDES: User's Manual,
Driver DVD, (2) SATA cables, I/O Shield. |

|
|
Chipsets: Intel H67
Express
CPU Support: Intel Socket
LGA1155
Memory Type: Dual Channel
DDR3
Videocard Support: (1) PCI Express
x16 2.0
Price at time of review: $107
USD | |
| |
As PCSTATS mentioned, the microATX Intel DH67BL motherboard is equipped with one PCI Express 2.0
x16 videocard slot that runs with 16-lanes of bandwidth; rounding out the expansion
slots are two PCI Express 2.0 x1 slots and one PCI slot. This MicroATX board
has four 1.35v dual channel DDR3-1066/1333 memory slots which can accommodate
up to 16GB of DDR3 RAM in 64-bit OS like Windows
7.
Connectivity includes two USB 3.0 ports, fourteen USB 2.0 (six at the
rear I/O, eight via internal header), one eSATA, one Gigabit network jack
and the standard assortment of Intel High Definition 8-channel audio (optical S/PDIF
included).
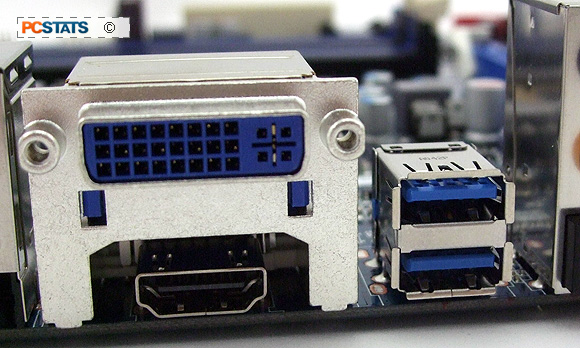
The integrated graphics ports on this motherboard include a DVI-I (capable of DVI and DVI-to-Analog with an adaptor) and
HDMI 1.4 jack.
The Intel DH67BL motherboard can
be found on retail shelves for around $107 CDN, ($107 USD, £70 GBP), a
little high for its vanilla feature set. Never the less, PCSTATS will
put this motherboard through its paces on both integrated graphics and a discrete graphics
card.
Before we get to benchmarking though, let's take a closer look at
what makes this motherboard tick.
Intel H67
Express Chipset
 As with Intel's P67
core logic, the Intel H67
Platform Controller Hub communicates with socket 1155 'Sandy Bridge' processors over a
20Gb/s DMI link. The H67 chipset contains eight PCI Express 2.0 lanes, the remaining system 16
PCI Express lanes stem from the processor.
As with Intel's P67
core logic, the Intel H67
Platform Controller Hub communicates with socket 1155 'Sandy Bridge' processors over a
20Gb/s DMI link. The H67 chipset contains eight PCI Express 2.0 lanes, the remaining system 16
PCI Express lanes stem from the processor.
Where the P67 and H67 chipsets diverge
is in regards to the integrated graphics core at the heart of the
Sandy Bridge 2nd Generation Core /3i5/i7 processor. The Intel P67 lacks
Intel's Flexible Display Interface (FDI) so it cannot
output video. Looking at the chipset block diagram below, you'd
be forgiven for thinking the Intel Z68, P67 and H67 chipsets are
fundamentally identical as the feature sets are very similar.
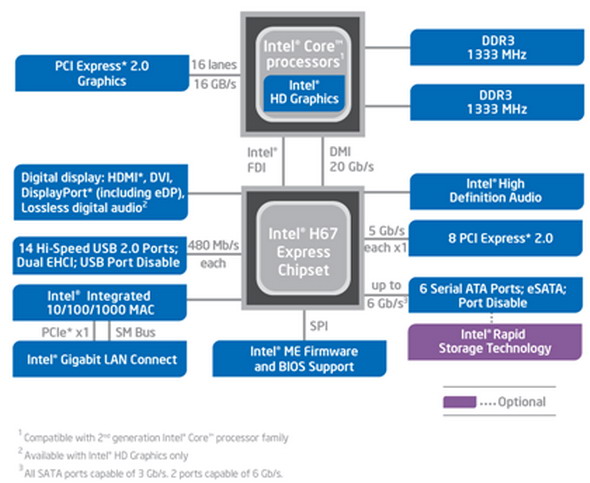
The Intel H67 and Z68 chipsets are closely related
too, however the Z68 picks up the tweaking features of the P67 and a few new tools
like Intel SRT which PCSTATS has extensively dicussed in previous articles (see: Intel
SRT and also here).
In addition to major changes like Intel FDI, the Intel H67 chipset continues
support for SATA 6Gb/s devices and slowly increases the number of USB 2.0 ports.
Still no USB 3.0 though.
| Intel Chipset Feature
Comparison |
|
Intel Z68
Express |
Intel P67
Express |
Intel H67 Express |
| CPU |
LGA 1155
Core i5/i7 2nd Gen. |
LGA 1155
Core i5/i7 2nd Gen. |
LGA 1155
Core i5/i7 2nd Gen. |
| Chipset Code Name |
Couger Point (65nm) |
Couger Point (65nm) |
Couger Point (65nm) |
| Bus Interface / Speed |
DMI 20Gb/s |
DMI 20Gb/s |
DMI 20Gb/s |
| Memory Support |
DDR3-1333, dual channel |
DDR3-1333, dual channel |
DDR3-1333, dual channel |
| Maximum Memory Capacity |
32GB (64-bit) |
32GB (64-bit) |
32GB (64-bit) |
| Integrated Graphics |
Yes. via CPU |
- |
Yes. via CPU |
| Integrated Graphics Ports |
HDMI, DVI, DP, VGA |
- |
HDMI, DVI, DP, VGA |
| PCI Express 2.0 Lanes |
8 |
8 |
8 |
| PCI Express x1 Lanes |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| Intel Rapid Storage Technology |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
| Intel Smart Response Technology |
Yes |
- |
- |
| SATA 6Gb/s | SATA 3Gb/s | IDE Ports |
2/4/0 |
2/4/0 |
2/4/0 |
| RAID |
0, 1, 5, 10 |
0, 1, 5, 10 |
0, 1, 5, 10 |
| Intelgrated LAN |
10/100/1000 MAC |
10/100/1000 MAC |
10/100/1000 MAC |
| USB 3.0 Ports |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| USB 2.0 Ports |
14 |
14 |
14 |
| PCI Masters |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| Intel High Definition Audio |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes | | |
Next up, PCSTATS looks at the integrated graphics
capabilities of the Intel H67 and Sandy Bridge processor, as well as Intel FDI
and Quick Sync....

