As part of the upgrade to the XP firewall, Microsoft added a more elegant
means of dealing with programs that need to act as servers. A server program
allows other computers to connect to it to share data, via a network or the
Internet. A good example of a program that needs to act as a server would be the
Kazaa file-sharing software.
Instead of creating a service which permanently opens a specific port, you
can now add programs to an exception list. Any program on this list will be
allowed to open ports when it needs them, unrestricted by the firewall.
This is both more intuitive and more secure.
To add a program to the
exceptions list, go to ‘start\control panel\windows firewall’ and choose the
‘exceptions’ tab.
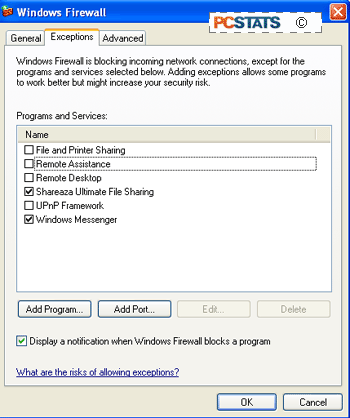
To enable an exception for a program or service listed here, place a
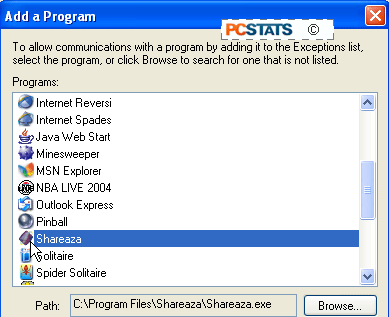
checkmark next to it. If the program you need is not in the list here, click
‘add program’ and scroll through the list until you find it.
Following the same principle, if you are
experiencing problems with any application not communicating properly after you
enable the XP firewall, in most cases you just need to discover the ports that
application wants to use and open them in the way we just displayed.
A list of common applications and ports follows.
Note that many of these applications, especially the file sharing ones, can be
configured to use many different ports. If this is the case, you can choose a
specific port to use yourself, and set it both in the application and in the
firewall settings so everything works.
 |
| Common Application Port Numbers |
| msn
messenger: |
ports 6891-6900 tcp for file transfer, 6901 tcp/udp for
voice (otherwise self configures messaging) |
| kazaa media
desktop: |
port 1214 tcp (can be reconfigured within kazaa) |
| shareza: |
port 6346 tcp (can be reconfigured) |
| icq: |
port 5190 tcp, at least one port between
1024-65535 |
| aol instant
messanger (aim): |
should self-configure |
| skype voip:
|
should
self-configure | |
for more of these, consult the website appropriate
to your software and look for firewall information, or bunker down and have a
look through the software's network settings for port options.
Allowing applications through the Zonealarm firewall
With the newest revisions of
Zonealarm, most common applications like MSN Messenger file transfer can be
allowed simply by giving them permission to act as a server in the 'program
control/programs' tab.
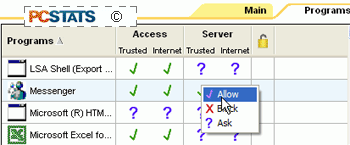
To do this open Zonealarm and
go to the 'program control' panel, then click the 'programs' tab. Scroll down
the list of programs until you find the one that is giving you problems. Left
click on the question mark in the 'server/internet' section of your
application's row. Change the setting to 'allow.'
Retest your application. It
should now work correctly.
Allowing common applications through Home
Internet sharing devices
Configuring home routers to
allow various applications to work correctly requires a different process for
each brand and type of device. Fortunately these procedures tend to be similar
to each other, so we decided to use a fairly typical example of these devices,
an SMC Barricade wireless home router, in order to illustrate the general
procedure.
Unfortunately, many common apps like MSN Messenger
file transfer often will not work through home router firewalls. This is because these devices generally
use NAT (Network Address Translation) to carry out their Internet sharing duties. NAT functions
by storing Internet data requests from computers inside the home network in a
table, then comparing the data received from the Internet to that table to see if
the source and data type matches.
If it does, the data from the Internet is forwarded
to the computer in the network that requested it. If not, it is dropped. The
trouble is that NAT only recognizes certain common data types and will not pass
on data that is not recognized. This leaves many file transfer and voice/video
conferencing programs out of luck.
If your Home Internet sharing
device has a 'special applications' page, or the equivalent, you can experiment
with opening the required ports for the application. In our experience though,
this tends to be a hit or miss procedure with NAT hardware firewalls. In this
case, research is your best chance for success. Do a web search on the
application looking for specific setup details.
Hosting websites, games and FTP behind your
firewall.
Hosting a website or game
server is a little different than using an application which may require special
privileges to get through your firewall. For one thing, when you are hosting,
it's implied that data traffic is coming from the Internet to your computer or
network, not the other way around. This is a problem to start with, because by
default, firewalls drop all unsolicited traffic from outside the network. If you
have a website, no one's going to see it without some changes...

