TASKLIST: This command will give you a quick list of the
processes currently running on your system. It can be configured to show a lot
more information than the Task Manager Window, so it's worth mentioning.
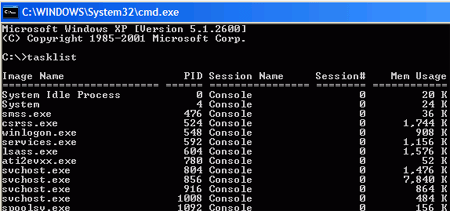
There are a lot of options and switches you can use to
order this information; two notable ones we use are: 'tasklist /svc'
which will show the services that are running under each process and
'tasklist /v' which gives a
more detailed (verbose) listing for each process.
SYSTEMINFO: This command can be used
to display essential information about your computer and its operating system,
including all installed patches, Service Packs and Hotfixes. SYSTEMINFO can also be
used on remote systems, and you can output the results to a CSV or table for use
in Excel or other spreadsheet programs by using the '/FO CSV' or
'/FO TABLE' switches in conjunction with the '>' filter which passes the results
to a file.
An example would be: systeminfo /fo csv >
c:\systeminfofile.txt
Which would output your system information to the c:\systeminfo.txt file in
CSV (Comma Separated Variable) format, which Excel can turn into a
spreadsheet.
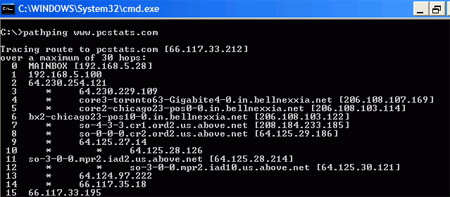
PATHPING: This command essentially combines the PING and
TRACERT commands into a single, potent network-tracing tool. In its
default usage, pathping will first list the number of hops (steps through
different routers or network servers) required to reach your destination IP
address or URL, then it will ping each step along the way 100 times, giving you
a clear idea of the speed of the connection between your system and your target
as well as any weak links in the network.
We hope you've enjoyed this quick guide to some of the
many useful functions the Windows command prompt can perform. If you have any
comments or suggestions, let us
know .
Find out
about this and many other reviews by joining the Weekly PCstats.com Newsletter today!
Catch all of PCstats latest hardware reviews right here.
