 Before we get to the various interesting things you can do with the command
prompt, we should first make sure that everyone is on the same level regarding
how to actually open and navigate it. With modern Windows PCs, it's quite
possible that many users have never even seen a command prompt, let alone
learned how to use one.
Before we get to the various interesting things you can do with the command
prompt, we should first make sure that everyone is on the same level regarding
how to actually open and navigate it. With modern Windows PCs, it's quite
possible that many users have never even seen a command prompt, let alone
learned how to use one.
Entering the Windows XP
command prompt
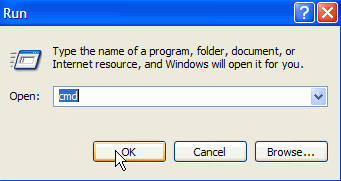
The easiest way to get to the command prompt is by opening up the run command
and typing 'cmd'. To do this: Open the start menu and click 'run.' In the text
box, type 'CMD'.
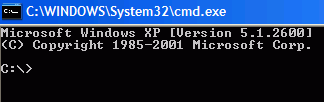 This will open the command
prompt, starting you off at the C:\documents and settings\(user
name)> prompt. To get to the root of the C: drive, type
This will open the command
prompt, starting you off at the C:\documents and settings\(user
name)> prompt. To get to the root of the C: drive, type
cd..
and press enter, then repeat this same step again. You will now be
looking at the C:\> prompt, meaning the root of your main hard drive,
just as if you'd opened 'my computer' and double clicked on drive (C:\).
Now let's look at how to get around in the command prompt's DOS-like
environment.
Navigating the Command Prompt
Like the Windows graphical environment you are used to, the command prompt
uses drives and directories (folders) to organize data. Each logical drive
(C:\, D:\, etc.) has it's own entry here, and contains its own set of directories
and files.
The command prompt window will place you at'C:\>' by default, meaning you
are looking at the logical 'C:\' drive, generally the first hard disk on your
computer and the one on which Windows is installed.
As an experiment, go to 'my computer' and open your c: drive in a
window. Now at the command prompt, type 'DIR'.
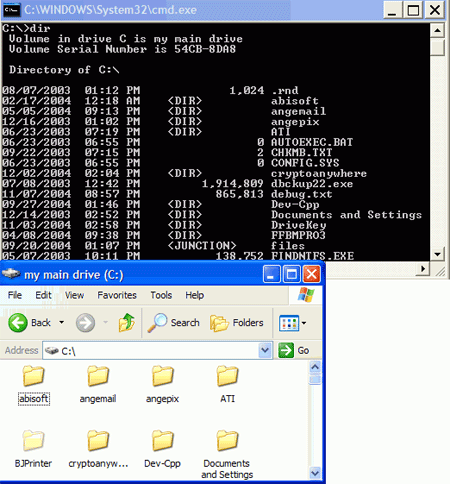
As you can see, the contents of both windows are the same, though the order will
be slightly different since Explorer puts folders before files, while the directory
(DIR) command simply lists all contents alphabetically.
The 'DIR' command lists the contents of the folder or drive you are currently
at in the command prompt. To get a more useful listing of the files
and folders in your current directory, use the 'DIR /d' or 'DIR /p'
switches. The former displays the list in three columns, fitting more info on a
single screen, while the latter pauses at the end of each screen of information,
waiting for you to press a key before it continues scrolling. Note
how the contents of the 'DIR' command are the same files shown in the Explorer
window on your desktop.

