If the
hard drive appears, but is missing a significant amount of space (say you are
seeing 20GB instead of 40GB) you are probably being limited by your mainboard
and will need to go to the drive manufacturer's website to download an
installation utility. Every hard drive manufacturer has a version of this
available. Maxtor's Maxblast3
software is one example. The purpose is to enable older mainboards with a
built in HD space limitation to overcome this.
As this software will also partition and format the
drives for you, it can be quite useful.
Assuming all is
well with the newly installed hard drive, all that remains is to partition
and format it. A partition is a logical grouping of the
space available on a disk that any operating system can recognize, while formatting a partition
enables a specific file system (FAT32 with Windows 98, or NTFS for NT/2000,
etc.) to read from and write to that partition, creating a logical drive (C:
in Windows is a logical drive).
In
general, any OS that supports the file system a partition is formatted with can
read and write to that partition. To partition and format in
Windows XP/2000, right click on 'my computer' and select 'manage.' Once you are
in the management screen, select 'disk management'.
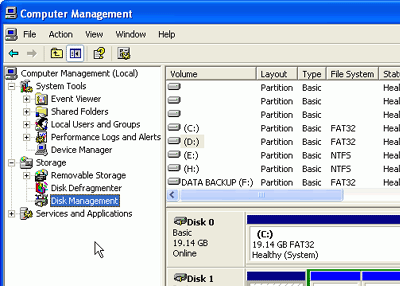
A screen showing your
existing drives, including the new one, will appear. At this point Windows should
open a wizard to help you partition and format your new drive. If it does
not, right click the new drive in the lower pane and select
'initialize drive.' Now you must partition the drive.
Right click
on the new drive and select 'new partition' to launch the partition wizard. You will be
prompted for how much space you wish to allocate to the new partition.
For the sake of argument, let's say we use the whole thing. You will then
be asked for a drive letter which Windows will use to represent
that partition, and prompted to format the drive.
Generally it's best to format with the NTFS file system unless you need to give
other computers with earlier versions of Windows, (or another OS installed on
the same computer) access to the new drive.
For
Windows 9x/ME users, you will need to use the FDISK utility, (found in the
C:\windows\command directory) to partition the newly installed hard drive and
assign it a logical drive letter so Windows can format it. Be careful
with FDISK, as it is quite easy to erase your existing partitions if you are
not sure of what you are doing.
Upon running FDISK, you
will be presented with the following screen.
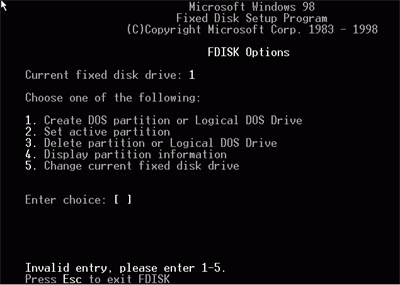
Select
(5) to view a list of all drives available on the system, then select
the new hard drive. Hit (1) to create a primary (first) partition on that drive.
Select (y) to use all the space on the drive and make the partition
active. Now exit Fdisk and reboot. Now you will need to format the drive.
After Windows loads, open 'my computer,' you
should see the new hard drive present as a logical drive (D:, E:, etc.). Right
click the new drive and select 'format.' Make sure quick format is not selected
and hit ok. After the procedure finishes, your drive will be ready for use.

