Before we go any further in this article, we should mention that
many Internet service providers consider hosting a website on a personal
Internet connection to be a violation of the user agreement. This is
especially true of cable-based service providers. In many cases though, a
personal website with a small amount of traffic is not an issue. Check the terms
of your service contract before hosting a website on a personal internet connection in order to avoid
unpleasant surprises later on.
Understanding IP addresses and DNS
In order to understand the rest of this article,
the function of IP and DNS addresses must first be grasped. If you feel know
these subjects already, feel free to skip to the next part of this Beginners Guide.
IP addresses: a computers' digits
An IP address is the computer's address on whatever network (including the Internet)
it happens to be on. Having a valid IP address allows a PC
system to send and receive data over a network correctly. This address
takes the form of four sets of decimal numbers, 0-255, for example:
192.168.5.45
Each network adaptor installed in a computer must have its own IP address, so it's
quite possible for a PC to have more than one IP address. To look
at a computer's IP address(es), open the command prompt (start\run and type
'cmd') then type 'ipconfig'.
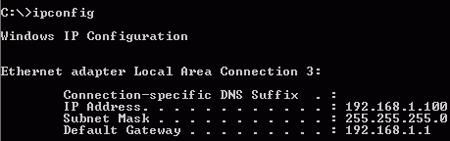 As we can see here, the IPCONFIG command shows three values for each IP address;
the address itself and a subnet mask and default gateway. The subnet mask
is used to separate each IP address into a host and a network portion. The
host portion of the address indicates the computer's exact address within its
network, while the network portion indicates the network the computer belongs
to.
As we can see here, the IPCONFIG command shows three values for each IP address;
the address itself and a subnet mask and default gateway. The subnet mask
is used to separate each IP address into a host and a network portion. The
host portion of the address indicates the computer's exact address within its
network, while the network portion indicates the network the computer belongs
to.
All computers with the same network portion of an IP address can communicate
with each other provided there is some way to transfer signals between them.
The Subnet Mask (of Zorro)
A subnet mask is shown in the
same format as the IP address (for example 255.255.255.0). As far as
this Beginners Guide is concerned, assume that the values of the 4 sets
of numbers in the subnet mask can be either 0 or 255.
Sets with
the value of 0 indicate the host portion of the IP address, and sets with the
value of 255 indicate the network portion. For example, with an IP address of
192.168.3.25 and a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0, the network portion of the
address would be '192.168.3', and the host portion would be '.25'. This means
the computer assigned this address is host 25 within the 192.168.3 network.

