The first
ever six-core socket AM3 processor from AMD has arrived, and with it AMD
can now directly compete against Intel's robust Core i7 9-series 'Nehalem'
chips. Code named 'Thuban', the new 3.2GHz
AMD Phenom II X6 1090T
processor introduces with it a dynamic overclocking technology
called TurboCore. In typical computing situations AMD TurboCore
will increase the speed of up to three of the Phenom II X6's CPU cores from
3.2GHz to 3.6GHz, while simultaneously increasing
processor voltage and dropping the speed of the remaining three unloaded cores.
The technology acts much like Intel TurboBoost and in benchmarks such as PCMark Vantage
AMD TurboCore does result in a noticeable performance boost.
In most respects though, the six-core AMD
Phenom II X6 1090T 'Thuban' processor builds upon the established Phenom II
X2/X4 'Deneb' architecture AMD has put to work for some time
now. Looking under the hood most AMD users will see familiar
specs such as 6MB of shared L3 cache and 512KB of L2 cache for
each of its six cores. The Phenom II's
multi-core design promotes a larger L3 cache that feeds faster L2
caches for the individual cores, a balance that improves multi-threading performance overall.
Manufactured by Global Foundries FAB 1 in Dresden Germany,
the AMD Phenom II X6 1090T is fabricated on the 45nm SOI process, likely making it the
last flagship chip to roll off the assembly line before AMD transitions to
32nm. Its die, estimated to be 346mm2
in size, contains ~904 million transistors. The CPU is rated for
a moderate Thermal Design Power of 125W that assures existing AMD heatsinks
can be used without concern.
AMD continues to engineer its Phenom II processor
family with socket AM2+ backwards compatibility in mind, and true to
form the Phenom II X6 1090T may be used on either socket AM2+ or AM3
motherboards. The CPU supports DDR2-1066 and DDR3-1333
memory thanks to its dual memory controllers, but is best at home
on socket AM3 motherboards built around the AMD 890FX or 890GX
chipsets. The CPUs HyperTransport 3.0 link continues to operate at 4.0
GT/s and its on-board 128-bit wide memory controller runs at 2GHz.
 |
|
|
AMD Phenom II X6 1090T Processor |
|
|

|
| Tech
Specs |
|
Phenom II X6 1090T
CPU
Cores: 6
Clock Speed:
3.2GHz
TurboCore: 3.6GHz
L1: 6x 128KB
L2: 6x 512KB
L3:
6MB
Multiplier: 16x-18x
Package: 938-pin
Socket: AM3 (AM2+)Core: 45nm SOI
Transistor: ~904M
Die size: 346mm2
Power: 125W
Vcore: 1.125-1.40V
Code: 'Thuban'
Cost: $285 USD
|

| |
The 3.2GHz AMD
Phenom II X6 1090T processor is priced at around $280 USD ($280 CDN, £165 GBP). In this review PCSTATS will put the Phenom II X6 1090T CPU through a full set of processor
benchmarks, with TurboCore enabled and disabled, and compare it against Intel's
Core i5 / Core i7 processors, not to mention the previous multi-core processors
from AMD's own stables. PCSTATS will also run power consumption tests to show
you how TurboCore can significantly increase PC power draw... First
though, lets take a look at what else AMD is doing to sweeten the deal for
Phenom II owners...
Introducing 'Thuban' - AMD's first six-core
Phenom II Processor
AMD's latest six-core architecture is code named
'Thuban'. The AMD Phenom II X6 1090T is an evolution of the
same "Deneb" architecture that AMD has put to work in its Phenom II dual-core
and quad-core processors, but scaled up to six full cores/six threads.
|
AMD Phenom II-series
processors |
|
Processor Models |
Thermal Design
Power |
Clock
Speed/Turbo |
Architecture/Size/
Cores |
Cache |
Price (USD) |
| AMD Phenom II X6
1090T |
125W |
3.2/3.6GHz |
Thuban, 45nm=258mm2
6-core |
9MB(3MB L2+ 6MB L3) |
$280 |
| AMD Phenom II X6 1055T |
125W |
2.8/3.3GHz |
Thuban, 45nm=258mm2
6-core |
9MB(3MB L2+ 6MB L3) |
$199 |
| AMD Phenom II X4 965 Black Edition
125W |
125W |
3.4GHz |
Deneb, 45nm=258mm2
4-core |
8MB (2MB L2 +6MB L3) |
$195 |
| AMD Phenom II X4 910e |
65W |
2.6GHz |
Deneb, 45nm=258mm2
4-core |
8MB (2MB L2 +6MB L3) |
$169 |
|
AMD Phenom II X2 555 |
80W |
3.2
GHz |
Calllisto,
45nm=258mm2
2-Core |
7MB (1MB L2 +6MB L3) |
$99 |
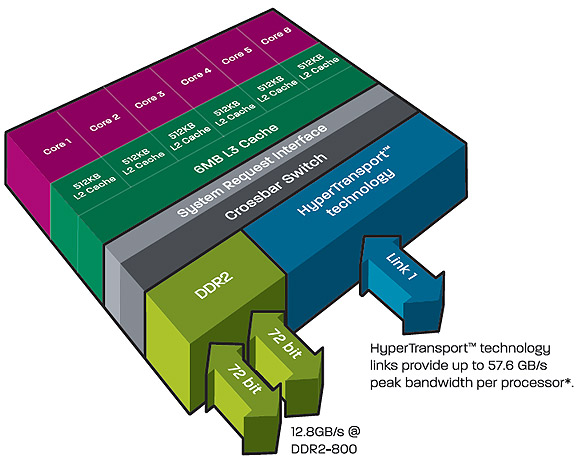
Like the rest of the Phenom II series, chips based on
the 'Thuban' architecture will have three levels of cache. Each individual core
will have its own 128KB of
L1 cache. This is the fastest possible cache and is split into two
64KB chunks for data and instruction sets.

Each core also gets its own
512KB of L2 cache, which in turn is fed by a larger 6MB L3 cache which is shared
between the six cores. The multi-core design of the Phenom II takes advantage of
a larger L3 cache that feeds faster L2 caches for the individual cores, which
increases both single core and multi-threaded performance.
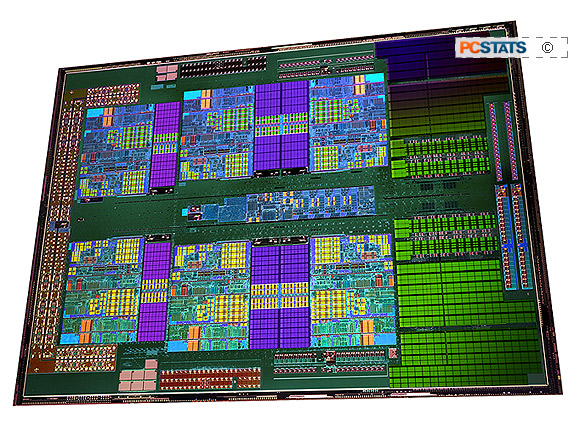
Processors based on the 'Thuban' architecture, like AMD's Phenom II X6 1090T, use HyperTransport 3.0
to communicate information from the processor to the system. HyperTransport 3.0 is
a 16-bit link that operates at 4.0GHz. The AMD Phenom II X6 1090T
also features a dual memory controller that will operate in DDR2 mode in socket
AM2+ motherboards, and in DDR3 mode when the processors is dropped into a socket
AM3 motherboard. The integrated memory controller is 128-bits wide and operates
at 2.0GHz, and supports DDR2 modules with speeds of up to DDR 1066MHz and DDR3
with speeds of up to 1333MHz.
While AMD won't release information on the AMD Phenom II
X6 1090T specific transistor count, the processor itself is still listed as
being produced on a 45nm processor with the same 346mm2 die size and 125W TDP as
AMD's previous flagship, the Phenom II
X4 965 Black Edition 125W. It's unclear what kind of voodoo sorcery AMD and
GlobalFoundries had to conjure to make a six-core chip fit into the same
die size and thermal envelope as its quad-core processors, but AMD does state that
you'll be able to upgrade to a six-core 'Thuban' processor like the AMD Phenom
II X6 1090T without the need for special cooling solutions or power supplies, a
stock socket AM3 heatsink-fan combo will be fine.
TurboCore -
AMD gets dynamic frequency adjustment
The introduction of the AMD Phenom II X6 1090T processor also introduces
TurboCore. Like Intel's Turbo Boost technology introduced in the Core i7
'Bloomfield' and Core i7/i5 'Lynnfield' processors, AMD's TurboCore technology
will increase the speed of individual processor cores automatically based on CPU
load and TDP levels.
By default TurboCore will increase the speed of up to
three CPU cores. One, two or three computational loads is enough to trigger
TurboCore, which will ramp up the loaded cores' speeds up to 3.6GHz, while
simultaneously increasing processor voltage, and dropping the speed of the other
three unloaded cores.
It's easiest to think of
TurboCore like this....

