DHCP
provides a means of easily setting up a network with little or no manual
configuration required. As such, it is a standard feature on home networking
devices such as cable/DSL routers. Assuming your home computers were set to automatically receive
IP addresses, as soon as you plugged your router in they would have received IP addresses
from it and been able to connect.
Of course, the presence of DHCP is one of the major reasons why wireless
networks are so insecure. Any computer that is able to communicate with
your router will receive an IP address automatically, and this address will put it
on the same network as all of your systems, enabling it to instantly access any unprotected
resources on your network such as shares.
Disabling DHCP is possible on all devices, but
it requires you to do some considerable manual configuration on your computers
in order to communicate. If you decide to disable DHCP, you must manually assign
each of your systems an IP address in the same network as the address of your
router. To do this in Windows XP:
Go to 'start/control
panel/network connections' and right-click on the connection you use to connect
to the router. Select 'properties'
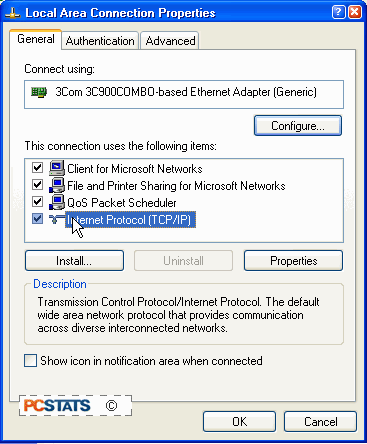
Highlight 'Internet protocol (TCP/IP) and hit the
'properties' button.
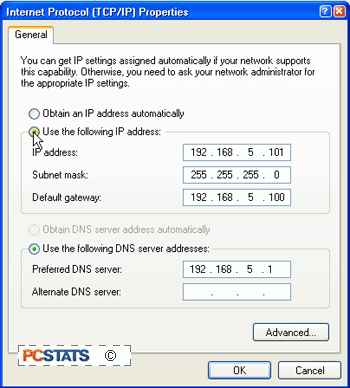
Select the 'use the following IP address' button, and
enter an IP address in the network you wish to use.
Most routers use network addresses
in the 192.168.x.y range, where x equals a number between 0 and 255 that indicates
the network, and y equals a number between 1 and 254 that indicates the
individual address of a computer or other device on that network.
So, if your router has an IP address of 192.168.5.100 and you have three computers, you could assign
them IP addresses anywhere between 192.168.5.1 - 192.168.5.254. Of
course, each computer must have a different address.
Accept 255.255.255.0 as the subnet mask. Enter the IP address of your router as the
default gateway. Click 'ok' to save the changes. If you disable DHCP on your
router, you should also change the default network that your router uses, since
this value is just as well known as the default username and password that each
manufacturer uses on their products. As mentioned, most routers use the
192.168.x.x IP address range for DHCP, so it's a good idea to pick a network ID
in this range, but less traveled, like say 192.168.65.x for your network.
Assure that your computers and
your router all have IP addresses in the same network, and that your computers
all have the IP address of the router as their default gateway. You should now
be able to communicate as before.

