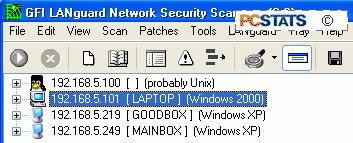
Now
examine the results for IP addresses generated
by the port scanning, and computers that do not fit your notes.
The 'net view'
command can be used to locate computers within the same workgroup as the
computer the command is run on. A workgroup is a simple logical grouping of
computers used by Windows. All Windows systems belong to the 'workgroup' workgroup
by default, so the 'net view' command can be very useful in finding out
which computers are currently attached to the network.
To use
net view: Open the command prompt
(start/run/'cmd'). At the prompt, type 'net view'
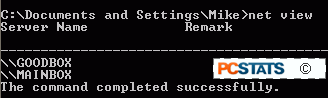
This will bring up
the names of all computers attached to the network that belong to the
same workgroup as your system.
If your
PC belongs to a different workgroup, you can change the net view command
to search for computers in other workgroups by typing Net 'view /domain:(the workgroup
name you wish to search)'. Scanning, as mentioned above, is a more reliable
method than net view however.
The Airsnare program is another excellent wireless (and wired)
intrusion detection program offered as freeware at this site.
It can be rather complicated to set up though, so we will not cover it further
in this article. Instructions can be found on the website for its use.
Checking your router logs and
connections
This is an important
step, but difficult to detail since it really depends on your hardware. Most
home routers will keep some sort of log file of recent connections and
connection attempts. Some will also log common 'bad' or unwanted Internet traffic such as someone
attempting to use a port scanner against your router's IP address.
Routers will
also generally keep a list of the systems they have given IP addresses to, which
would indicate whether you have any unwanted guests on your network.

