This step is optional; if your system does not have a RAID or serial ATA hard
drive controller, or you do not use them, skip it. This method will work
with almost all simple RAID/SATA controllers such as the ones commonly
included on desktop motherboards and add-in PCI controllers. It may or may
not work with 'business class' RAID adaptors, depending on the model.
If your system uses a RAID or Serial ATA controller to operate your hard
disks, the Windows install process cannot 'see' these disks without the proper
drivers for the RAID or SATA controller. Normally you would press 'F6'
immediately upon starting the install, which informs the system that you are
using a disk controller that needs drivers. The install process would then
pop up a request for the drivers on a floppy disk. Once the drivers are
provided, the installation continues as normal.
If you don't have a floppy drive though, or want to perform an automated,
unattended install of Windows XP, you need to find another way of
providing the necessary drivers to the install process.
Before you do anything else, you need to make sure that your RAID or SATA
controller recognizes the drives that are plugged into it. Observe the
RAID/SATA BIOS screen during bootup for information. If your drives are
not being found, consult your product documentation for instructions. Once
the drive controller has recognized your hard drives, we can continue.
In this step, we will download the necessary drivers for your RAID/SATA
controller and integrate them into the Windows XP source files so they load
automatically after the CD boots.
Step 4A: Copying SATA/RAID drivers into the
Operating System files
First, download or copy the drivers for your SATA/RAID controller into a
subfolder within the 'bootcd\drivers' folder. If they are in a zipped
file, extract them. Many driver packages contain subfolders for each
operating system, so navigate to the correct one for your OS.
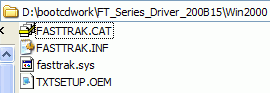
You need at least four files, the .sys, .inf, .cat files and the txtsetup.oem
file. The 'txtsetup.oem' file may be in a different location than the rest
of the files, but there should only be one. There may well be additional
files present, and these should also be included in the following procedure.
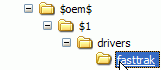
Now navigate to the 'bootcd\working' directory and
create a folder called '$OEM$'. Inside the $OEM$ folder, create a folder
called '$1'. Inside the $1 folder, create a folder called 'drivers.'
Next create a folder within the 'drivers' folder named for your SATA/RAID controller ('fasttrak' for example).
The $OEM$ folder and its contents are used to store additional drivers and
software that are to be added to Windows during the install process.
Copy and paste all driver files you downloaded earlier
into the 'bootcd\working\$OEM$\$1\drivers\(SATA/RAID controller name)
' directory you just
created. This will allow these drivers to be accessed by the setup
process, once we make a few more changes.

