Now that you know basically what a service is, let's
take a look at what services are running on your computer. To
access a configurable list of services, open the Start menu and click the
'run' command.
In the text box, type: services.msc
and hit ENTER. This will bring up the services
management window.
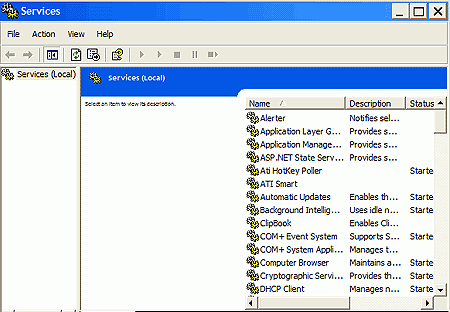
Maximize the window and take a good look at it. As you can see, there
are a lot of services present in a standard Windows XP environment (we'll go
through which ones are supposed to be there and what they do later in the
article); note that each service has a name and a useful description
attached to it, as well as having 'status,' 'startup type' and 'log on as'
attributes.
'Status' simply indicates whether a given service is actually running on your
computer at the moment. Services are either 'started' or not.
'Startup type' indicates how starting the service is handled by Windows.
There are three possible values:
Automatic: The service is started automatically as part of the Windows
XP boot process.
Manual: The service can be started by another application or process
that needs it, but is off by default. Once it is started, the service will
remain on until it is manually stopped or the system is rebooted.
Disabled: The service will not start unless this condition is
changed.
Finally, the 'log on as' attribute determines which user or system account
the service uses to perform its duties. This can have several
implications, but is more important for those who are designing new
services. As you can see, most of the services use the 'local system
account' which provides them practically unlimited access to your computer, but
does not allow them to perform any operations over a network. Services can
also be run under users accounts, which gives them the same security permissions
as that specific user would have.

