The rear of the case is
certainly quite interesting. Starting from the middle left users will find the onboard audio connectors for
the 7.1-channel speaker configuration, the line-in port and optical SP/DIF in/out jacks. On the bottom left is the motherboard
clear CMOS button, a very nice feature for those who like to push the
limits!
There is
also a standard IEEE 1394 jack, the PS/2 connectors, TV output (S-video), LAN and two USB
slots, a VGA and DVI monitor connector (a block of jumpers on the inside selects between the
PCI-E x16 slot and the onboard DVI jack) and the six-pin 12V DC power
connector.
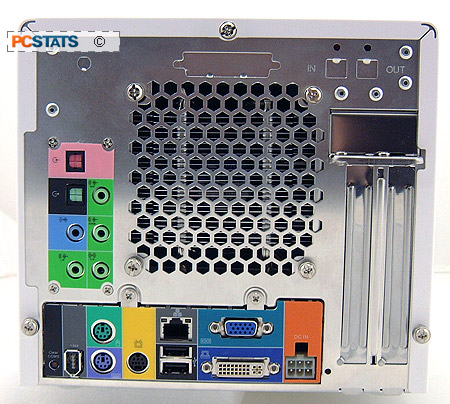
To the right of that are
the two expansion slot openings for the PCI Express devices. There are also a couple knock-outs at
the top of the aluminum chassis for an optional wireless LAN antenna and parallel
port.
Filling up most of the space on the rear of the Shuttle XPC
SD11G5 is a large honeycomb exhaust vent for the 'Integrated Cooling Engine'
(ICE) heatsink. The honeycomb pattern has been shown to allow air to pass
through it with the least amount of turbulence. It's important that users leave
enough space behind the computer so that airflow from this vent is not
restricted.
 Shuttle
'Integrated Cooling Engine'
Shuttle
'Integrated Cooling Engine'
The ICE
heatsink works in conjunction with a speed controlled 92mm fan, that
according to the manufacturers acoustic test report, produces about 24.5 dBA with 'smart fan' settings
enabled.
At full speed, noise levels from the fan may reach
upwards of 43.8 dBA.
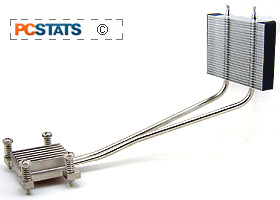 The ICE thermal solution mounts onto the processor with
a custom-spaced set of screw-points, and transfers the heat about 8 inches to the back of
the SFF PC where the fan is located.
The ICE thermal solution mounts onto the processor with
a custom-spaced set of screw-points, and transfers the heat about 8 inches to the back of
the SFF PC where the fan is located.
What makes the ICE heatsink tick are a set of nickel plated
copper heatpipes that bridge the distance between the processor and the stacked
aluminum fin heat exchanger. The heatpipes are soldered to a copper baseplate
that makes direct contact with the silicon core of the Intel Pentium M processor
(thermal compound is included). There is a foam ring on the base of the
heatsink to help prevent the core from being chipped.
