The current dual-core systems from Intel and AMD both use SMP (Symmetrical
Multi-Processing). SMP is the most common approach to creating a multi-processor
system, in which two or more separate processors work together on the same
motherboard. The processors coordinate and share information through the system
bus, and the processors arbitrate the workload amongst themselves with the help
of the motherboard chipset and the operating system. The operating system treats
both processors more or less equally, assigning work as
needed.
Each processor within the die functions as an independent unit, and it is the
responsibility of the motherboard and chipset to coordinate them and exchange
data between them when necessary.
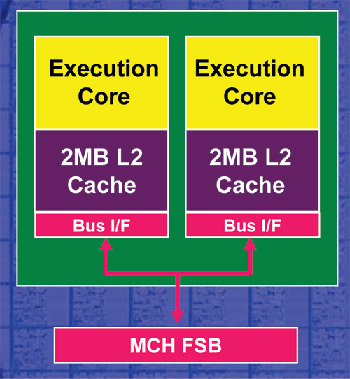 Intel's approach forces both processors
to communicate through the Northbridge and FSB outside the processor die which
is different from the internal communication method used by AMD for its dual-core Athlon
64 processors.
Intel's approach forces both processors
to communicate through the Northbridge and FSB outside the processor die which
is different from the internal communication method used by AMD for its dual-core Athlon
64 processors.
There's been some contention
that this method is less efficient and will bring down the performance
slightly, but we'll see some actual numbers later in the article to settle that question. What
we can say for sure is that Pentium D processors like higher
memory speeds, regardless of actual FSB speed; dual channel PC2-8000 DDR memory is the bare
minimum realistically.
What Does Multiprocessing Offer?
Software can be defined as either single-threaded or multi-threaded, with a
'thread' being a set of operations the processor is performing on a portion of a
given program at a given time. Single-threaded programs are designed to allow
only a single thread to be operated on at any one time, whereas multi-threaded
programs can separate different portions of the work that needs to be done by
the processor(s) into different threads.
Single-threaded programs derive no major benefit from multiple-processor
systems, but the system as a whole benefits because the second processor can
continue to operate while the first processor is using 100% of its time on a
single program or error. Multi-threaded applications can share their load
between multiple processors, allowing different parts of the program to be
executed at the same time, and thus derive the largest benefit from
dual-processor systems.
Dual processor systems also gain from a general decline
in latency. Simply put, while there is no current way to share the current
operating system load evenly between two processors, the second processor can
step in and keep the system running smoothly while the first is maxed out to
100% burning a CD or
encoding a file (or from a software error).
To sum up, any modern operating system will see at least some benefit from
running with more than one processor, even when that OS is running
single-threaded applications only. This benefit will be specific to certain
applications and conditions though, not a general speed boost.
