The bare PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards), with solder paste
applied in the right places, take the second step
towards becoming fully-fledged motherboards here. The SMT (Surface Mount
Technology) machines pick and place the tiny resistors, solid-state capacitors
and other IC (Integrated Circuit) chips onto the PCB at ultra high speeds. If you
look at the motherboard in your computer, some of these small components are no
more than 1mm square!
Each board passes through two sets of FUJI CP742
high speed SMT machines, the 'small pick and place' and 'large pick and place'
devices. Each machine in the set adds a few components, from tiny resistors up
to the North and Southbridge chips. Belt fed from tape-like cartridges
of components, the SMT gear places components like a machine gun,
taking as little as an eighth of a second to place a component with exact precision
on the PCB.

Gigabyte's
SMT production lines |
All chipset ICs, plus the BIOS chips and any integrated
peripherals (but not their connectors) are added to the top of each
motherboard-to-be during this step of the process. The PCB then passes through a
Heller 1900EXL hot convection oven to fully melt and set the solder paste,
securing the components in position. Motherboards that require components to be
placed on the underside of the board are now flipped and sent through the solder
screen printing and SMT process again.

The FUJI pick and
place SMT machines mount components on each motherboard
|

components
are fed into the SMT machines from tape-like reels
|
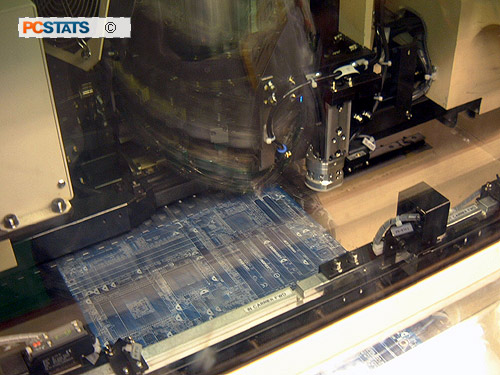
An SMT
machine about to start placing components on a motherboard
|

Each of the 16 or so
heads places a different component in
as little as 1/8 of a second (flash frozen in this picture)
|

