The motherboards now go through an AOI (Automated Optical Inspection)
machine which will catch any obvious SMT or soldering defects.
They are then visually inspected by a worker using a plastic mask, so that
they can easily spot any missing or misaligned components.
Finally the motherboards undergo an 'in-circuit test' which involves
testing each motherboard's circuit paths, electrical characteristics
and the chips that have just been added by applying electrical current
to certain specific test points on the board. Each motherboard is placed
on a special rack and a testing board is lowered onto it, making contact
with the motherboard at specific points. Current is applied, and the
results are analyzed by the technician running the station. The whole process
takes less than a minute.
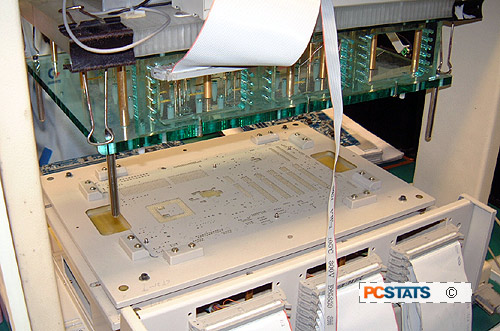
The Gigabyte in-circuit
electronic test bed |
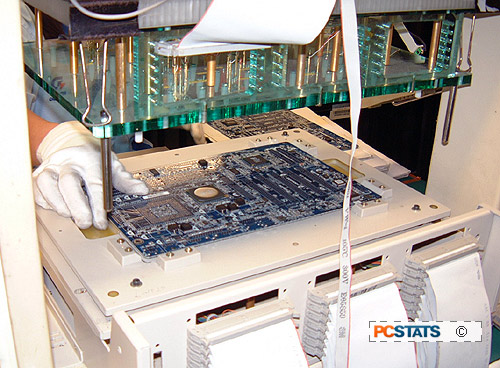
Each board is mounted on the test bed...
|
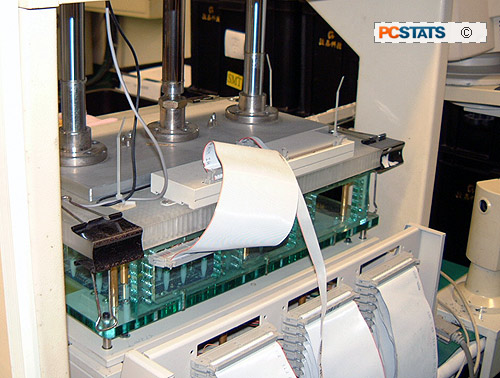
The
rack is lowered, making contact with test points on the board
|

Assorted spare
test rigs gathering dust on a shelf |

A different rig is
needed for every motherboard model Gigabyte produce.
This in-circuit tested is for the Gigabyte GA-8KNXP motherboard. |

