32. Create a RAID
configuration on your system to boost hard disk performance
If you are using Windows XP Professional or Windows 2000
and you have more than one hard drive installed, you can create a RAID 0
'stripe' to speed up hard disk performance.
RAID, or Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks, is a
technology that allows for data to be dispersed among two or more hard disks at
once, providing additional speed or additional data security or both depending
on the configuration. While the more sophisticated forms of RAID are
intended for corporate setups, Windows XP Professional includes the most basic
RAID configuration, RAID 0, as part of the package.
RAID 0, or 'data striping,' takes two disks or portions
of two disks and turns them into one 'logical' drive that the computer can
address (like C:). All data written to that drive is split evenly between
the two drives. Since both drives can be written to or read from at once,
this increases data transfer speed.
A RAID 0 setup requires at least 2 hard drives, each with
some unpartitioned space. For complete instructions on creating a RAID 0
setup on your Windows XP system, see PCstats RAID article here. The action begins
on page 5!
33. Disable the themes
service
If you are not a
fan of the appearance of Windows XP, there is an easy way to turn it off and go
back to the more sober and traditional Windows style. Simply disable the
'themes' service to restore a classic windows desktop appearance.
To do this, right
click on 'my computer' and select 'manage.'
In the computer
management windows, expand 'services and applications' and select
'services.'
In the right hand
window, highlight the 'themes' service. Right click it and select
'properties.'
In the 'startup
type' dropdown box, select 'disabled.'
34. Remove the desktop
picture
Your desktop background consumes a fair
amount of memory and can slow the loading time of your system. If you are more
concerned with performance than looks, remove your picture and go with a blank,
coloured background.
Right click on an
open area of the desktop and select 'properties.'
Select the
'desktop' tab and in the 'background' window, highlight 'none.' Press 'ok.'
v
Think we're just pulling your leg? Nope, every computer
in the PCstats labs that gets tested goes through this same step before we run a
single benchmark.
35. Change to the NTFS file
system
If you are using
Windows XP, it's a good idea to convert your system drive to the NTFS file
system if you have not already. In addition to providing numerous security and
data recovery improvements over FAT32 (the file system of choice for Windows
9x/ME and XP Home) it can also speed up your system slightly.
In fact, the only
real reason for sticking with the FAT32 file system for any of your data is if
you have more than one operating system on your PC and the other OS's can only
see FAT32 partitions (as would be the case with Windows 98, for example, which
is incapable of reading NTFS data).
To convert
your drives to NTFS:
Right click on 'my
computer' and select 'manage'
From the
computer management window, expand storage and select 'disk
management.'
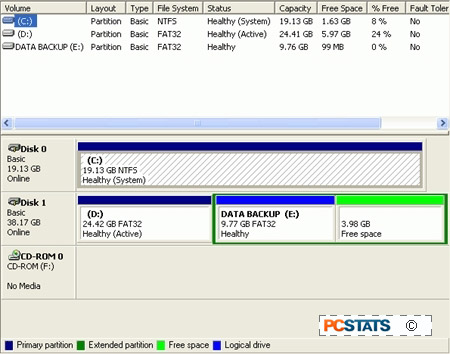
Using the
'file system' column of the upper pane of this window, you can easily check what
file system each of your logical drives is using. Make a note of this
information.
Now open
a command prompt window by going to 'start\run' and typing 'cmd'
To
convert a disk to NTFS, type 'convert (drive letter): /fs:ntfs'
So for
example, if you were going to convert your C: drive, you would type 'Convert c:
/fs:ntfs' at the prompt.

