60. Displaying hidden files
and folders
By
default, many of the important system files and folders in Windows XP are
hidden, meaning they cannot be seen by navigating with explorer. User created
files can also be hidden. A simple option change enables you to see all hidden
files and folders with Windows explorer.
To view
hidden files and folders: Open 'my computer' and click on the 'tools' menu item.
Select 'folder options,' then the 'view' tab. Under the 'hidden files and
folders' selection, choose 'show hidden files and folders.' Press 'ok.'
61. Convert Your drives to the NTFS file
system
The NTFS
file system is the default file system used by Windows NT\2000\XP PRO\Server
2003. Unlike its predecessor, the FAT32 file system seen in Windows 9x/ME, it
allows for effective security settings on individual files and folders by using
ACLs or Access Control Lists. These are a list of permissions placed on each and
every file, listing which users are allowed to access the file and what they are
allowed to do with it.
On top of
its security advantage, NTFS drives are also easier to recover data from in the
event of an emergency. NTFS drives are also a requirement for several features
of Windows XP. As there is no effective performance difference between NTFS and
FAT drives, it is recommended that you convert your logical drives to NTFS. This
can be done one way only, as NTFS drives cannot be converted back to FAT 32.
If you
are using Windows XP Professional, chances are your drives are already formatted
with NTFS, as this is the default. XP Home still defaults to FAT32 however.
The only
situation where it is not advisable to convert a drive would be in situations
where multiple operating systems reside on the same computer. If one of these
operating systems is unable to read NTFS (such as windows 9x/ME) it will lose
access to the drive that has been converted to NTFS. If the converted drive
contained that operating system's files, it will no longer be able to
boot.
To
convert your drives to NTFS: Right click on 'my computer' and select 'manage'.
From the computer management window, expand storage and select 'disk
management.'
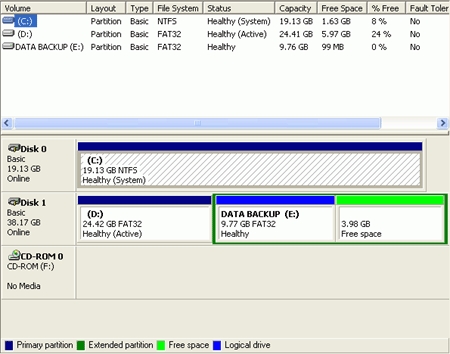
Using the
'file system' column of the upper pane of this window, you can easily check what
file system each of your logical drives is using. Make a note of this
information.
Now open
a command prompt window by going to 'start\run' and typing 'cmd'. To convert a
disk to NTFS, type: 'convert (driveletter): /fs:ntfs'.
So for
example, if you were going to convert your C: drive, you would type:
'Convert c: /fs:ntfs' at
the prompt.

