50. Scan your computer for
vulnerabilities with Microsoft's free security scanner
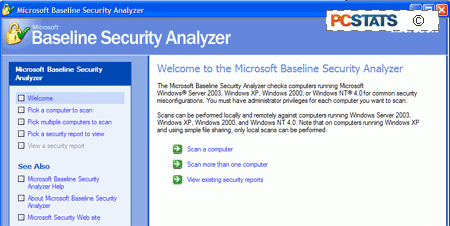
Microsoft provides a tool called the Baseline Security
Analyzer (MBSA) to help network administrators or concerned users check their
machines for security vulnerabilities. The software is available here.
Download and run the
device to test both your local computer and any PCs on your network (you will
need access to an administrative account on all machines you wish to scan). The
MBSA creates a security log for each scanned computer which contains easy to
read info on any vulnerabilities that may exist and how to correct them.
PCSTATS
highly recommends that you use this tool to check your PC for security flaws.
Also see PCstats Ten Steps to a Secure PC article for more information on essential
computer security steps.
51. Disable USB Storage
Device Writing (Service Pack 2)
USB storage devices are very easy to use in Windows XP.
Since they use the built-in mass storage drivers, anyone can just plug in a
memory key and download whatever they want onto it. This can be a security
concern for both business networks and home users who let others have access to
their PCs. This is especially true because of the large amount of information
that can be put on the typical memory key, and the speed of their use.
If you are concerned about this issue, Windows XP
Service Pack 2 contains a feature that lets you combat it. You can now make USB
storage devices read-only, meaning that no one will be able to move data onto
them.
To make USB mass-storage devices read only:
Open Regedit and navigate to 'HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\
CurrentControlSet\Control key'
Highlight the subkey 'StorageDevicePolicies' If there is
no such subkey, create it by right clicking 'control key' and choosing
'new\key'. Once you have the 'StorageDevicePolicies' subkey highlighted, right
click it and select 'new\ DWORD value.' Give the value the name WriteProtect.
Double click the new value and give it the value of '1' Exit and restart.

