42. Disable hibernate on
desktops
If you've got a desktop that's on most of the time, doing
large amounts of non-critical applications in the background (read downloading),
you probably want to disable the hibernation and hybrid-sleep functions of
Vista. Doing so will save you a chunk of disk space the size of your physical
RAM.
To turn off hibernation in
Windows Vista:
Open the 'start menu' and type 'cmd' in the search bar
but do not press Enter. Right click on the 'cmd' shortcut where it appears in
the search results and choose 'run as administrator'.
In the command prompt, type 'powercfg h off'.
43. Stop scheduled disk
defragmentation
Microsoft has considerably simplified the disk
defragmentation interface in Windows Vista, and made it an automatic process,
figuring (probably accurately) that 99% of their user base does not know what
disk defragmentation is and would not do it anyhow.
By default, Windows Vista will run a disk defragmentation
process (essentially making sure that all the files on your drive occupy
contiguous drive space and are not scattered all over the surface of the
physical disk) every Wednesday morning at 1AM. If you happen to be up gaming at
1AM on Wednesday morning, this will play havoc with your frame rates. It's
probably better to disable the automatic defragmentation process and do it
manually once every 3-6 months.
To disable automatic disk
defragmentation in Windows Vista:
Open the 'start' menu and type 'defrag' in the search
bar. Hit 'Enter'.
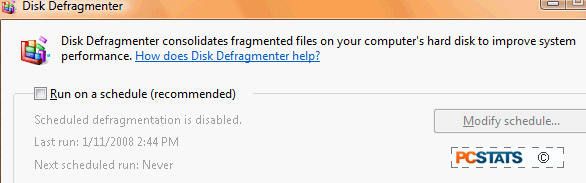
Uncheck the 'run on a schedule' check box.
Click 'ok'.
44. Move the Vista paging file for better performance
The page file is an area of hard disk space reserved by
Windows for use as additional memory. By default, Windows manages and resizes
this file dynamically to suit its needs. Vista does a very good job of
optimizing the page file on its own, but there is one tweak you may be able to
make which will considerably increase its performance. If you have more than one
physical hard disk drive installed in your computer, you can move the page file
onto the physical drive that does NOT have Windows Vista installed on it. Since
most page file hits are related to Windows system operations, this will
considerably reduce disk access on your OS drive, speeding everything up.
 To move the Windows
Vista Page file:
To move the Windows
Vista Page file:
Click on the 'start' menu and right click on 'computer'.
Choose 'properties'.
In the left-hand pane, choose 'advanced system
settings'.
Click the 'advanced' tab, then under the 'performance'
heading choose 'settings...'
Choose the 'advanced' tab again, then under the 'virtual
memory' heading click 'change...'
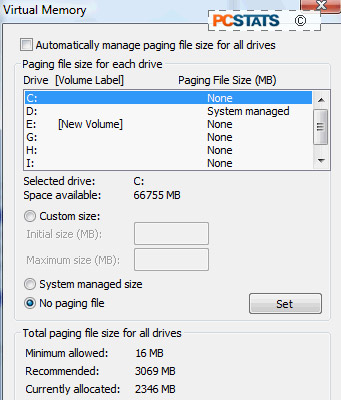
Uncheck the 'automatically manage paging file size for
all drives' checkbox.
In the window that shows the list of partitions (C:, D:,
etc.) choose a partition that resides on the physical hard drive that does not
have Windows installed and highlight it. Select the 'system managed size' option
then click the 'set' button. This will create a paging file on the hard disk in
question.
You will notice that the 'paging file size' for the
highlighted drive now reads 'system managed'
Now highlight your C: partition (assuming that this is
where Windows Vista is installed). Select the 'no paging file' option and click
'set'.
Your paging file has now been offloaded.

